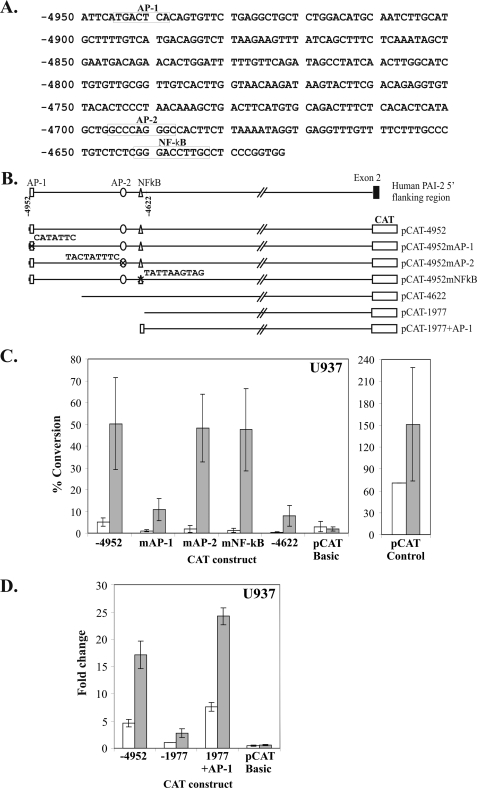
FIGURE 2.
A distal AP-1 site at −4952/−4932 is necessary and sufficient for human PAI-2 transactivator activity in U937 cells. A, nucleotide sequence of the 330-bp transactivator region between −4952 and −4623 showing the positions of consensus sequences for AP-1, AP-2, and NF-κB elements. B, schematic diagram of the mutant transactivator CAT reporter gene constructs showing mutations at positions −4945/−4939 (AP-1), −4696/4688 (AP-2), and −4642/−4633 (NF-κB). In addition, pCAT-1977+AP-1 consists of a minimum (21 bp) region containing the AP-1 element inserted into pCAT-1977 in the wild-type orientation. C, CAT reporter gene analysis of constructs in U937 with or without PMA showing that the AP-1 site is required for transactivator activity. D, U937 cells transiently transfected with the indicated expression plasmids with or without PMA, showing that the 21-bp AP-1 site is able to derepress promoter activity. CAT activities are reported as the percentage conversion of chloramphenicol normalized to the average value for untreated pCAT control. The results represent the mean ± S.E. from at least three independent transfections performed in triplicate.