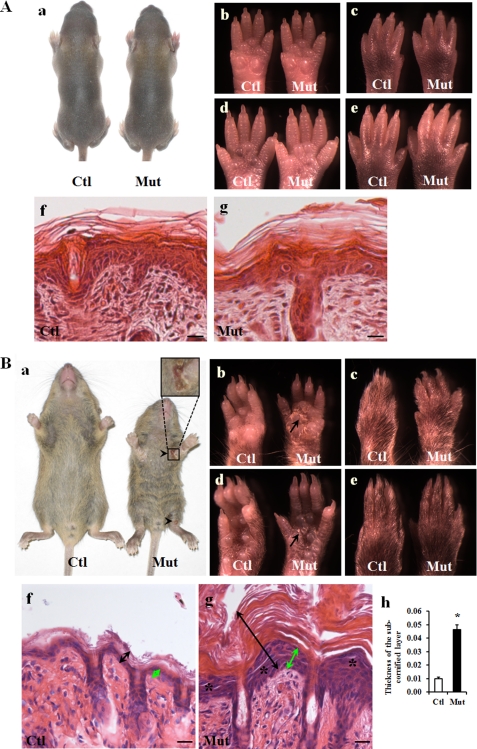
FIGURE 1.
Epidermal phenotypes of Jup mutant mice. A, normal epidermis of 1-week-old Jup mutant mice. Panel a, general morphology of a Jup mutant (Mut) mouse and a control (Ctl) mouse. Panels b–e, normal appearance of the Jup mutant palm and planta. No apparent plaques are visible. Panels f and g, normal histology of control and Jup mutant epidermis, respectively. Scale bars = 20 μm. B, Jup mutant mice develop an abnormal epidermal phenotype at ∼2 weeks after birth. Panel a, general morphology of a Jup mutant mouse and a control mouse (16 days old). The Jup mutant is smaller than its control littermate, and the hair on the Jup mutant abdomen is rough. Ulcerations (arrowheads) are seen near joint areas. The Jup mutant palm exhibits severe hyperkeratosis with plaques (panel b, arrow), whereas keratosis is mild in the Jup mutant planta (panel d). No apparent plaques are visible in either the Jup mutant opisthenar (panel c) or instep (panel e). Jup mutant epidermis (panel g, double-headed black arrows) is markedly thicker than control epidermis (panel f), with a thick, shedding cornified layer and thickened subcornified layer (double-headed green arrows). Detachment of granular layer (asterisks) is apparent in Jup mutant epidermis. Scale bars = 30 μm. Quantitation of the thickness of the subcornified layer is shown in panel h. *, significantly different from the control (p < 0.01; n = 4 (control) and n = 3 (mutant)).