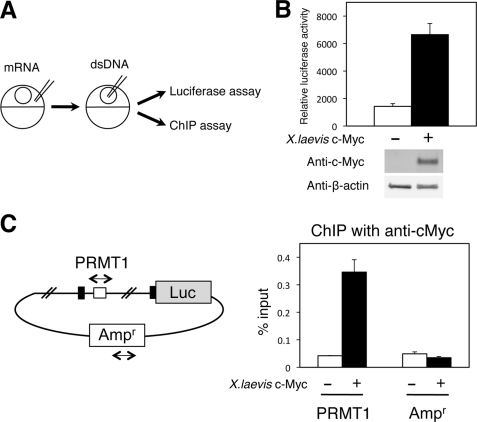
FIGURE 5.
X. laevis c-Myc directly binds to the first intron of the X. laevis PRMT1 gene to activate the promoter in vivo. A, schematic diagram of the Xenopus oocyte transcription system. The mRNA encoding X. laevis c-Myc was injected into the cytoplasm. A few hours later, the double-stranded firefly luciferase reporter and the control Renilla luciferase vector (dsDNA) were injected into the nucleus. After overnight incubation, the oocytes were lysed for luciferase activity measurement, and ChIP assays were carried out. B, c-Myc activates the PRMT1 promoter. The full-length PRMT1 promoter construct was analyzed in the oocyte in the presence or absence of overexpressed c-Myc. A Western blot analysis was also performed on the same lysate with anti-c-Myc and anti-β-actin antibodies, indicating the expected expression of c-Myc in the injected oocytes (bottom panel). C, c-Myc is bound to the first intron of the PRMT1 gene. Oocytes as in B were subjected to a ChIP assay with a c-Myc antibody to determine the association of c-Myc with the first intron (PRMT1) as well as the ampicillin-resistant gene region (Ampr) in the same plasmid as a negative control. The black and white boxes show exons and the putative c-Myc biding site in the X. laevis PRMT1 gene. The immunoprecipitated DNA was analyzed by quantitative PCR.