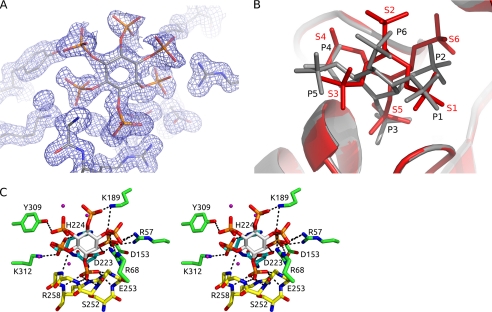
FIGURE 1.
InsP6 ring conformation and electron density. A, 2Fo − Fc electron density contoured at 1.5 σ for the InsP6 bound in the active site. B, superposition of the PhyAsrC252S·InsP6 complex (gray) and the PhyAsr·MIHS complex (red; PDB code 1U26). InsP6 binds in a chair conformation with the C2 phosphate in an axial position and the remaining phosphates in equatorial positions. The C3 phosphate is bound in the active site consistent with known specificity of this enzyme. MIHS binds with the C2 phosphate in an equatorial position and with the C5 sulfate in the active site. C, divergent stereo view of the interactions between InsP6 and PhyAsrC252S. Residues involved in InsP6 binding are shown as sticks, and dashed lines represent specific hydrogen bonding or electrostatic interactions. The P-loop (yellow) accounts for all backbone contacts with InsP6, whereas the GA loop (cyan) and six additional residues (green) make direct contacts through their side chains.