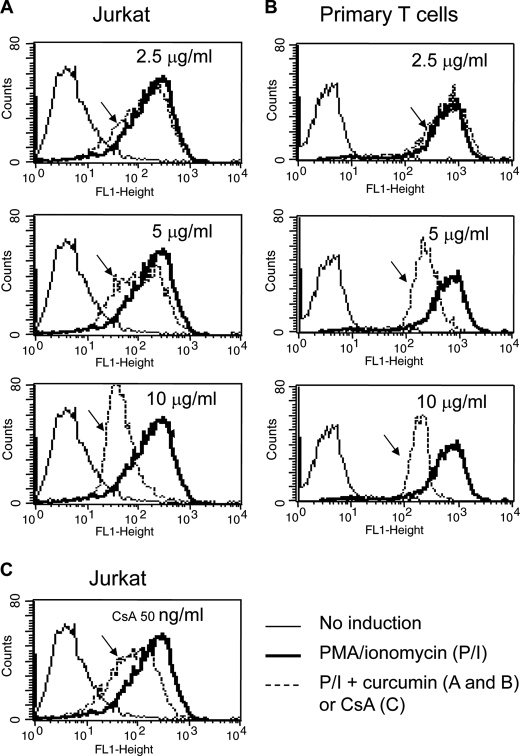
FIGURE 1.
Curcumin suppresses CD69 expression in activated T cells. A and B, curcumin suppresses CD69 expression in T cells. Jurkat (A) and freshly isolated human peripheral blood T cells (B) were stimulated with PMA (5 ng/ml) and ionomycin (1 μm) in the absence or the presence of 2.5 to 10 μg/ml curcumin as indicated. After 24 h stimulation, the cells were analyzed for CD69 surface expression levels by FACS. C, CsA suppresses CD69 expression. Jurkat T cells were stimulated with PMA and ionomycin in the absence or presence of CsA (50 ng/ml) as in A and B. The reduced CD69 expression is indicated by arrows. Results are representative of two independent experiments.