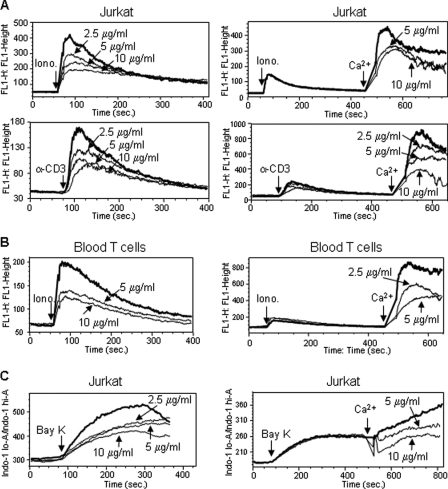
FIGURE 6.
Curcumin blocks Ca2+ mobilization in activated T cells. A, effect of curcumin on Ca2+ mobilization in Jurkat T cells. Jurkat T cells were loaded with 1 μm fluorescent Ca2+-indicator Fluo-4 in PBS in the absence of extracellular Ca2+ followed by pretreated with different doses of curcumin for 10 min. Cells were washed with PBS. The release of Ca2+ from the intracellular stores was measured by flow cytometry after adding ionomycin (1 μm) or αCD3 (OKT3 10 μg/ml) (left panels). For determination of influx of extracellular Ca2+, the intracellular Ca2+ stores were first depleted in the absence of extracellular Ca2+ by ionomycin or by αCD3 for 7 min. The cells were then treated with or without curcumin for 30 s. The Ca2+ influx was measured after adding 1 mm Ca2+ (right panels). B, effect of curcumin on Ca2+ mobilization in peripheral blood T cells. Blood T cells were treated as in A. C, effect of curcumin on Ca2+ mobilization in Jurkat T cells stimulated with (±)-Bay K 8644. Jurkat T cells were loaded with 1 μm indol-1 and pretreated without or with curcumin as in A. The Ca2+ levels were monitored by flow cytometry after adding 100 μm (±)-Bay K 8644. All data are representative of at least two independent experiments.