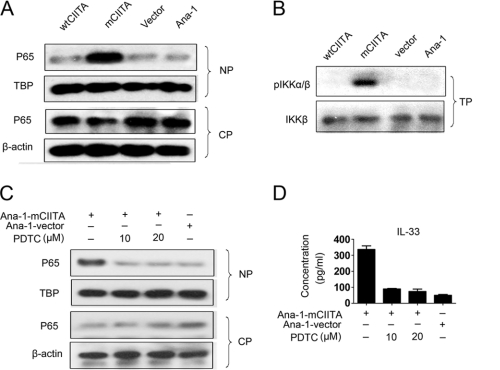
FIGURE 5.
Activation and translocation of NF-κB are associated with the Nod2-initiated signaling pathway. A, the translocation of activated NF-κB p65 protein to the nucleus was indicated by differential patterns of p65 expression in nuclear proteins (NP) and cytoplasmic proteins (CP). β-Actin and TBP (TATA-binding protein) were used as controls. B, phosphorylation of IKK-α/β (pIKKα/β) was detectable in the total protein (TP) fraction of Ana-1-mCIITA cells by Western blotting. Total IKK-β was used as a control. C and D, when pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate, an inhibitor of NF-κB activation, was introduced, the translocation of p65 in the nucleus (C) and the IL-33 production level in culture supernatants (D) of the Ana-1-mCIITA cells were substantially inhibited. After selection by 400 μg/ml G418 for 2 weeks, the cells were cultured for another 3 days in the presence of pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate at doses of 10–20 μm/ml and assayed for p65 by Western blotting (C) and for IL-33 by ELISA (D).