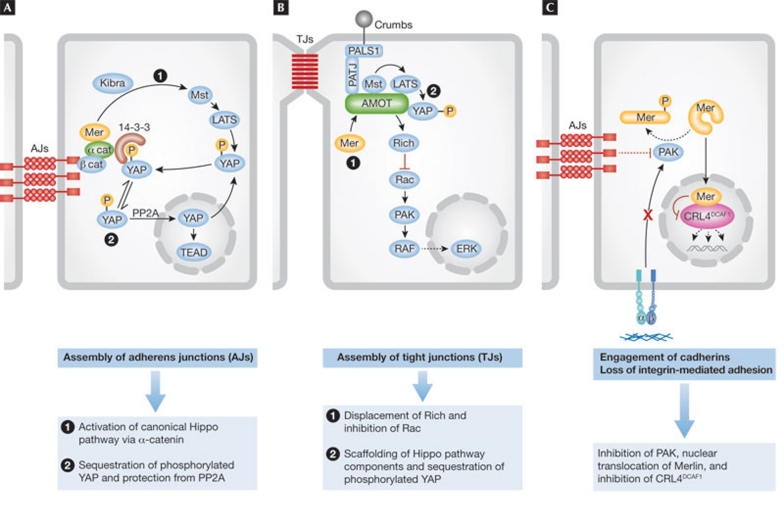
Figure 4. Emerging mechanisms of Merlin-mediated epithelial adhesion, polarity and inhibition of proliferation.
(A) Merlin (Mer) is recruited to nascent adherens junctions by α-catenin and contributes to the activation of Hippo signalling by cooperating with Kibra to activate the classical core kinase cascade, or by enabling α-catenin to sequester phosphorylated YAP in the cytoplasm through 14-3-3 proteins. (B) Upon assembly of tight junctions, Merlin binds to Angiomotin and displaces the Rac GAP Rich, thereby inhibiting Rac. In addition, Merlin might assist Angiomotin in coordinating the activation of the Hippo core kinase cascade. (C) Engagement of E-cadherin or loss of integrin-mediated adhesion leads to inactivation of PAK, promoting an accumulation of the de-phosphorylated (active) form of Merlin. Active Merlin enters the nucleus and inhibits the E3 ubiquitin ligase CRL4DCAF1, thereby suppressing the expression of multiple pro-oncogenic genes. CRL4, cullin-ring E3 ligase 4; DCAF1, DDB1- and CUL4-associated factor 1; ERK, extracellular-signal-regulated kinase; LATS1/2, large tumour suppressor 1/2; Mst1/2, macrophage stimulating 1/2; PAK, p21-activated kinase; PALS1, protein associated with Lin-7 1; PATJ, Pals1-associated tight junction protein; Rac, Ras-related C3 botulinum toxin substrate; TEAD, TEA domain family member; YAP, Yes-associated protein.