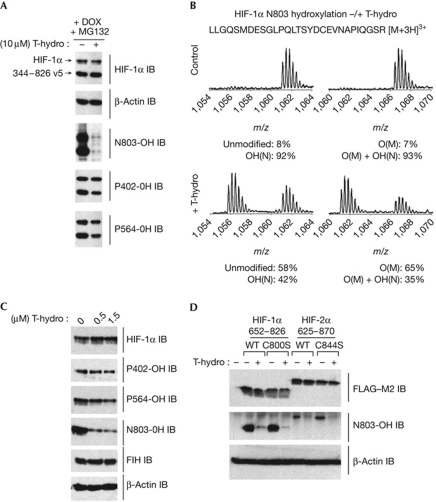
Figure 1.
Treatment of cells with peroxide reveals preferential inhibition of N803-OH compared with P402/P564. (A) Immunoblotting (IB) of extracts from U2OS 344–826 V5 cells treated with MG132 and −/+T-hydro at 10 μM for 3 h. (B) Mass spectrometry (MS) of purified 344–826 V5 confirms inhibition of N803-OH by T-hydro. The N803 tryptic peptide is shown with summed spectra for both its hydroxylated, OH(N) and unmodified [M+3H]3+ precursor ions. Methionine-oxidized forms of the peptide ‘O(M)’ are separated by chromatographic retention time and their spectra are also displayed. Percentage hydroxylation was calculated using the area under extracted-ion chromatograms for these ions. (C) N803-OH is more sensitive to inhibition by peroxide in RCC4 cells. (D) C800 is not required for peroxide-dependent inhibition of N803-OH. Weak crossreactivity of the anti-N803-OH antibody enabled assessment of the effects of C844 in HIF-2α. Dox, doxycycline; FIH, factor inhibiting hypoxia-inducible factor; HIF, hypoxia-inducible factor; OH, hydroxylation; T-hydro, tert-butyl hydroperoxide; WT, wild type.