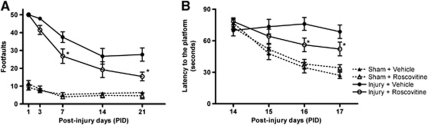
Figure 2.
Roscovitine treatment improves functional recovery after TBI. (A) Fine-motor coordination deficits were quantified using a beam walk test. Hindlimb foot placement was recorded and the number of mistakes (foot faults) was recorded from 50 steps. Roscovitine treatment significantly improved fine-motor coordination at 7 (*P=0.01 versus vehicle) and 21 days (*P=0.0025 versus vehicle) after TBI. Analysis by repeated-measures one-way ANOVA, followed by post hoc adjustments using Tukey's test (interaction: F=4.58; groups: F=104.82; time: F=19.17). (B) Spatial learning and memory was assessed using a Morris water maze test. Roscovitine-treated mice had reduced latency to locate the submerged platform at days 16 (*P=0.005 versus vehicle) and 17 after TBI (*P=0.02 versus vehicle). Analysis by repeated-measures one-way ANOVA, followed by post hoc adjustments using Tukey's test. (interaction: F=4.63; groups: F=20.99; time: F=12.89). Mean±s.e.m.; n=11 to 12 per group. ANOVA, analysis of variance; TBI, traumatic brain injury.