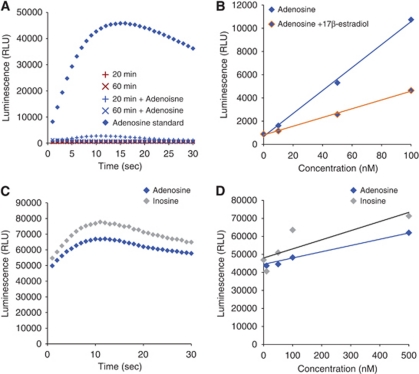
Figure 2.
Anomalies in use of the chemiluminescent adenosine assay. (A) Spiking of samples drawn from hypoxic cells shows an inconsistent ability to detect the presence of normally detectable adenosine concentrations. The ability of the assay to function normally and detect adenosine (500 nmol/L) is abolished after cells are exposed to 20 or 60 minutes mild hypoxia. (B) Addition of known free-radical scavengers at low concentrations dampens assay luminescence. (C) Lack of the sensitivity in single-step procedure. The luminescence intensity detected from inosine (500 nmol/L) was similar to adenosine (500 nmol/L) by using single-step procedure. (D) Single-step procedure failed to distinguish inosine (10 to 500 nmol/L) from adenosine (10 to 500 nmol/L).