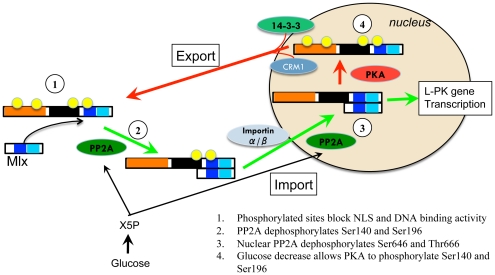
Figure 1. Phosphorylation model depicting ChREBP response to glucose.
Image adapted from [29]. 1) In low glucose conditions, sites S140/S196/S626/T666 are phosphorylated and block the NLS and DNA binding activity. 2) Upon glucose stimulation, X5P activates PP2A to dephosphorylate S140/S196 in the cytosol, unblocking the NLS, and allowing ChREBP to enter the nucleus. 3) Nuclear PP2A dephosphorylation of S626/T666 increases DNA binding. 4) Decreased glucose levels increase PKA activity to phosphorylate S140/S196 and shuttle ChREBP back to the cytoplasm.