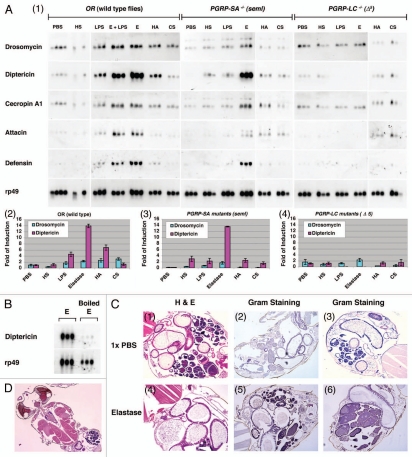
Figure 1.
Elastase activates the IMD pathway through the receptor PGRP-LC. (A) Expression of antimicrobial peptides (AMP) was examined in triplicate in wild-type OR flies and mutant flies, PGRP-LC (Δ5 null) and PGRP-SA (seml), after treatment with sterile 1X PBS, elastase (3 Unit/ml), LPS (40 µg/ml), heparan sulfate (HS, 5 mg/ml), hyaluronic acid (HA , 20 mg/ml) or chondroitin sulfate (CS, 20 mg/ml) overnight. Northern blot analysis was performed using 50 µg total RNA extracted from the treated flies, and the blots were hybridized with 32P-labeled cDNA probes to antimicrobial peptides including Drosomycin, Diptericin, Cecropin A1, Attacin, and Defensin. rp49 mRNA was used as a control. No bacteria were added in these experiments to induce IMD activation. Film exposure is in the linear range. AMP production was examined by northern blots (panel 1). The relative levels of AMP expression, Diptericin/rp49 and Drosomycin/rp49, are shown in bar graphs in wild-type and mutant flies (panels 2, 3 and 4). Note that elastase was sufficient to induce robust IMD activation, whereas the saccharides did not. (B) AMP production in OR flies treated with elastase (3 U/ml) and heat-inactivated elastase (boiled at 100°C for 5 min) was examined. Note that the loss of elastase enzymatic activity is associated with loss of IMD activation. (C) PBS- and elastase-treated flies were embedded in paraffin blots. The intestinal morphologies of 1X PBS- and elastase-coated adult flies are shown. Hematoxylin and Eosin staining (H&E) is used to view adult abdominal morphology/cellular histology using serial paraffin sections (panels 1 and 4). Gram staining was used to detect for the loss of structural integrity of elastase-treated flies and the presence of commensal bacteria in internal organs post elastase treatment (panels 2, 3, 5 and 6). Note that there is no bacterial presence outside of the intestines of elastase-treated flies when compared with PBS-treated flies, demonstrating that the intestinal integrity remains intact at the microscopic level and no commensal bacteria leaked into the internal organs upon elastase treatment. (D) Section shows the general morphology of adult retina, brain, heart and muscles, demonstrating that paraffin section can be easily adapted for Drosophila research of host-pathogen interaction.