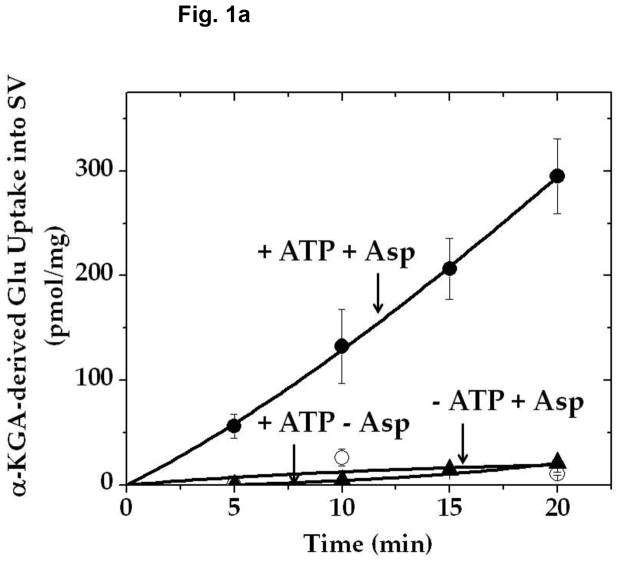
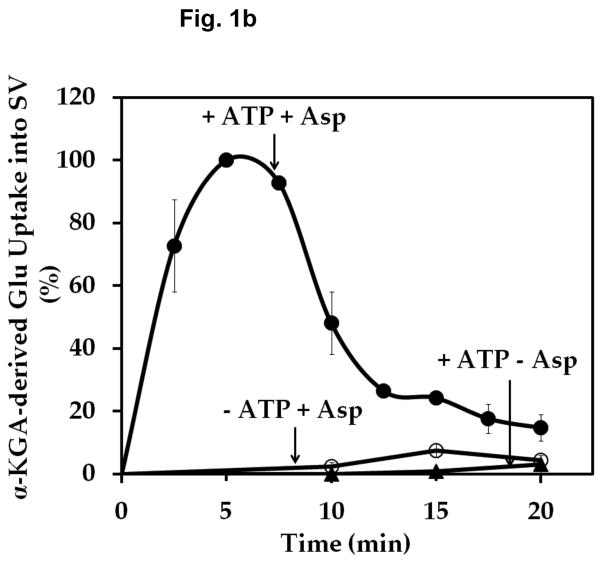
Fig. 1.
Time course of α-KGA-derived glutamate uptake into isolated synaptic vesicles. Rat synaptic vesicles (a) or bovine synaptic vesicles (b), 100 μg protein each, were preincubated at 30° C for 2 min in the medium containing 250 mM sucrose described in Materials and Methods, in the absence (○) or presence (●) of 2 mM ATP each with 2 mM L-aspartate, or in the absence of aspartate but in the presence of 2 mM ATP (▲). Following addition of 60 μM [14C]α-KGA, incubation was continued at 30° C for the various periods of time indicated. Vesicular accumulation of radioactive material was determined, as described in Materials and Methods. The value (72 ± 10 pmol/mg) obtained in the absence of ATP with 0 min incubation was subtracted from all values in each experiment shown in (a), and the value (40 ± 5 pmol/mg) from all values in each experiment shown in (b). The results in (a) show the mean ± SEM from three separate rat brain SV-A′ preparations, and those in (b) the average in percentage of two separate bovine synaptic vesicle preparations; 100% represent 215 ± 65 pmol/mg. SV, synaptic vesicle; Glu, glutamate; Asp, aspartate.