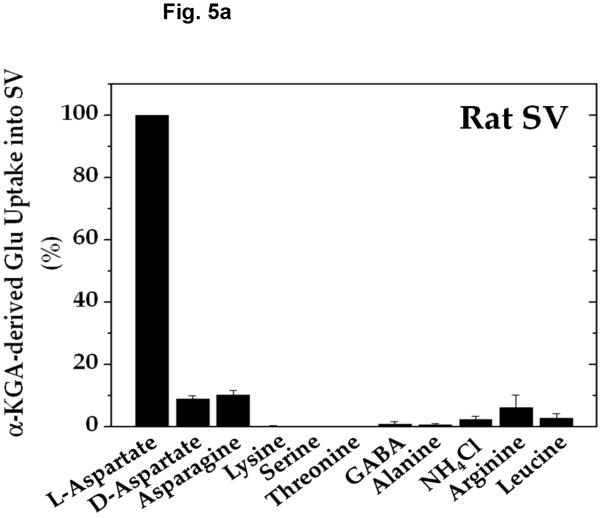
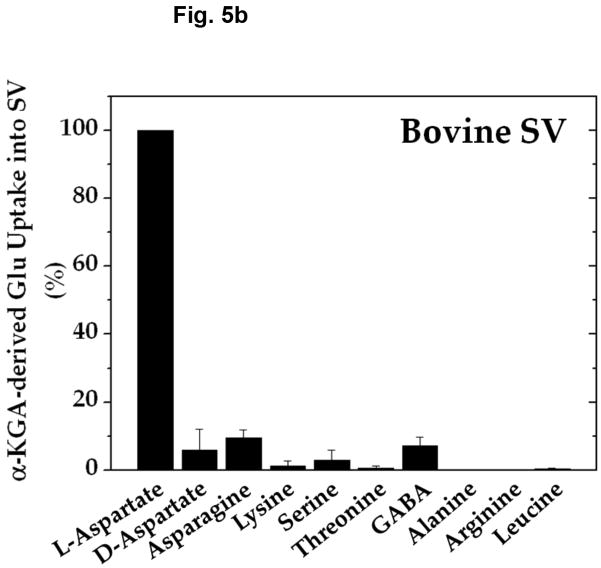
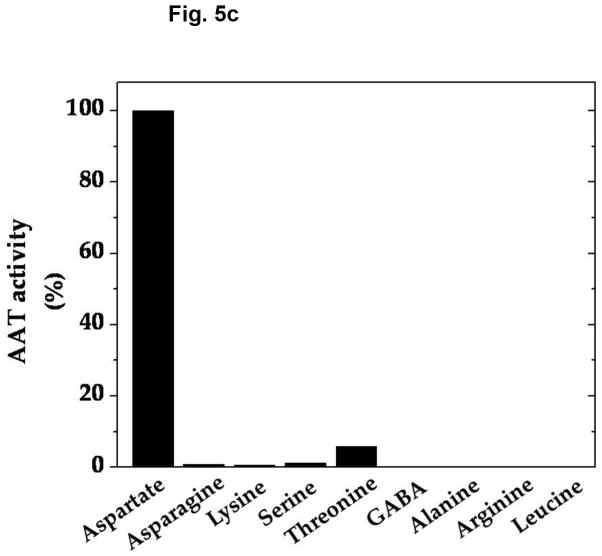
Fig. 5.
Amino-group donor specificity of vesicular α-KGA-derived glutamate uptake and vesicle-bound AAT enzyme activity. (a) Rat vesicular α-KGA-derived glutamate uptake. Rat synaptic vesicle fraction SV-A′ (50 μg protein) was incubated at 30° C for 15 min with 30 μM [14C]α-KGA in the presence of the indicated amino group donors, in the vesicular uptake medium containing 100 mM sucrose, as described in Materials and Methods. All amino donor agents were tested at 2 mM. The results are expressed as percentage of activity in the presence of 2 mM ATP with 2 mM L-aspartate (238 ± 59 pmol/mg, n=3). Values obtained in the presence of 2 mM ATP without aspartate were subtracted from all values. Each value represents the mean ± SEM, obtained using three separate preparations, except for D-aspartate (triplicates with one preparation). Glu, glutamate. (b) Bovine vesicular α-KGA-derived glutamate uptake. Bovine synaptic vesicles (100 μg protein) were preincubated at 30° C for 2 min, without [14C]α-KGA, in the vesicular uptake medium containing 250 mM sucrose. After addition of 30 μM [14C]α-KGA, the mixture was incubated for additional 3.5 min. The results are expressed as percentage of activity in the presence of 2 mM ATP with 2 mM L-aspartate (112 ± 49 pmol/mg, n=2). Values obtained in the presence of 2 mM ATP without aspartate were subtracted from all values. (c) AAT activity. Rat synaptic vesicle fraction SV-A′ (46 μg) was incubated at 30° C for 2 min to determine AAT activity in the presence of various amino donors (50 mM) in the medium described in Materials and Methods. The results are expressed as percentage of activity with 50 mM L-aspartate (122 nmol/min/mg).