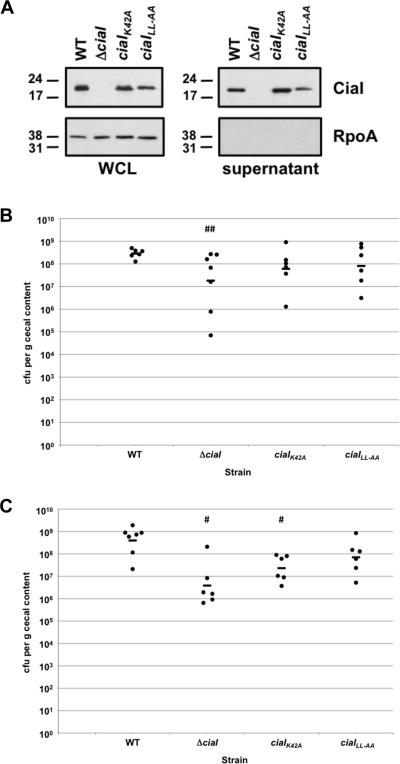
Figure 7. Analysis of the commensal colonization capacity of C. jejuni ciaI mutants.
(A) Production of CiaI proteins in bacteria and supernatants after growth in MH broth. Wild-type C. jejuni 81-176 SmR and isogenic mutants lacking ciaI, or containing ciaIK42A or ciaILL153-153AA (ciaILL-AA) were inoculated in MH broth and grown for 4 h at 37 °C in microaerobic conditions. Proteins from whole-cell lysates (WCL) and supernatants were recovered and examined by immunoblot analysis using antiserum specific CiaI or RpoA. For both WCL and supernatants, equal amount of proteins were loaded across strains. Molecular weight markers are indicated in kDa. (B and C) Commensal colonization capacity of wild-type C. jejuni 81-176 SmR and ciaI mutants. One-day old chicks were orally inoculated with 104 cfu (B) or 102 cfu (C) of C. jejuni strains. Each dot represents the amount of C. jejuni recovered from the ceca of each chick seven days post-infection. The geometrical mean for each group is depicted by the horizontal bar. Statistical analysis was performed using the Mann-Whitney U test (## P < 0.05; # P < 0.01). For wild-type C. jejuni and the ΔciaI mutant, the same data is shown as in Figure 5A and 5B.