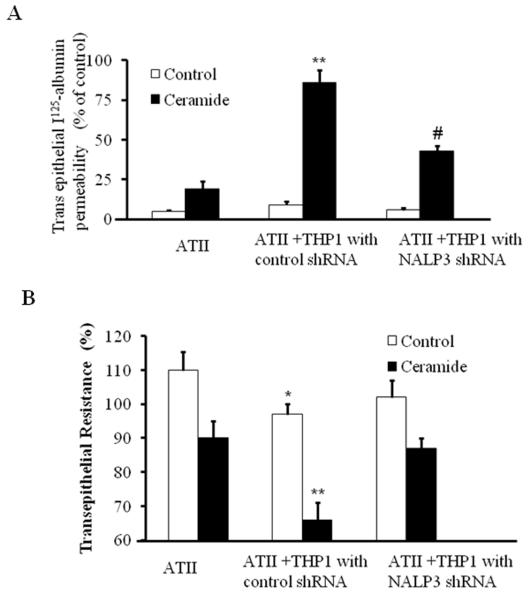
Fig 4. Inflammasome silencing inhibited ceramide induced transepithelial albumin flux in alveolar epithelial type II cells.
(A) ATII cells were grown in 24-well transwell plates until the cellular monolayers reached confluence. THP-1 cells were added to the appropriate ATII monolayers, cocultured for 6 h, and exposed to ceramide for 12 h. In some experiments, THP-1 cells were transfected with control shRNA or NALP-3 shRNA and then added to a monolayer of ATII cells. Transepithelial albumin flux across each monolayer was determined by the addition of [125I]-labeled human serum albumin to each upper compartment. The contents from the lower compartment were collected and counted in a Wizard γ-counter. *p<0.01 relative to AT-II cells; #p < 0.05, relative to control shRNA. (B) Effect of inflammasome silencing on TER in AT-II and THP-1 cells. ATII cells were grown in 24-well transwell plates until the cellular monolayers reached confluence. THP-1 cells were added to the appropriate ATII monolayers, cocultured for 6 h, and exposed to ceramide for 12 h. In some experiments, THP-1 cells were transfected with control shRNA or NALP-3 shRNA and then added to a monolayer of ATII cells. TER was measure by an epithelial voltammeter. *p<0.01 relative to AT-II cells; **p < 0.05, relative to NALP-3 shRNA. The noted experiments are representative of a minimum of three similar evaluations.