Figure 6.
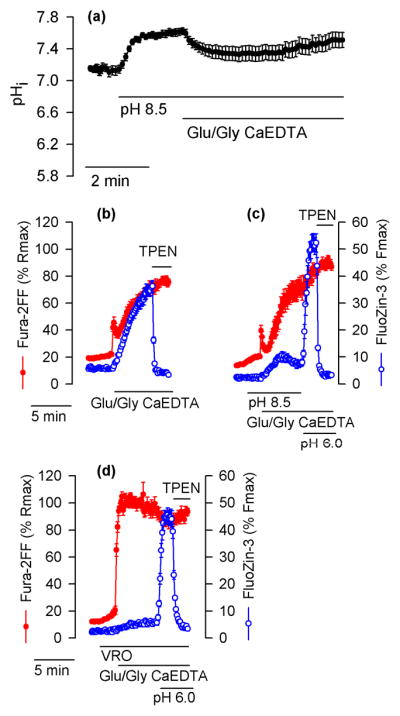
Alkaline pH inhibits and acidic pH promotes intracellular Zn2+ release in Glu/Gly-treated neurons. (a) The effect of alkaline pH on pHi in cultured hippocampal neurons exposed to Glu/Gly in the presence of 1 mM CaEDTA. The experiment was conducted as those shown in Figs. 4c and 5c (control, black traces) except that where indicated extracelluar pH was increased from 7.4 to 8.5. (b) Fura-2FF and FluoZin-3 signals monitored in a control experiment performed at a pH of 7.4. (c) Analogous experiments with Glu/Gly applied at the pH of 8.5 followed by application of a pH of 6.0. To ensure a prompt drop of pHi to 6.0, 5 μM gramicidin was applied at the time the extracellular pH was switched form 8.5 to 6.0. Where indicated, 10 μM TPEN was added to chelate Zn2+. (d) Similar experiment to the one shown in (c) but performed in the presence of VRO. The data are averages ± SE from 16 (a), 28 (b), 17 (c), and 22 (d) neurons monitored in a single experiment. All experiments were repeated with similar results 4 – 5 times.
