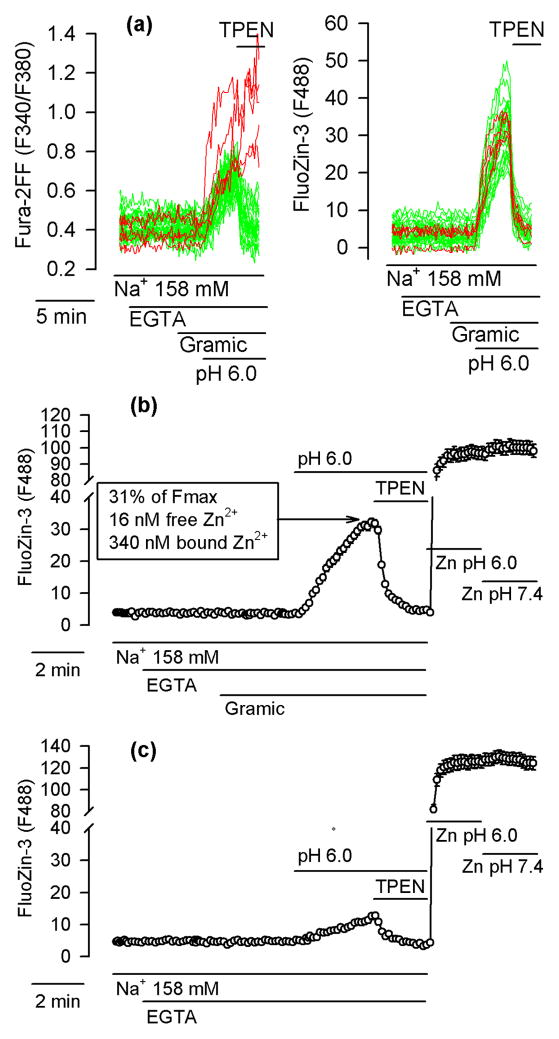
Figure 7.
A pHi drop (without Ca2+ influx) suffices to induce intracellular Zn2+ release. (a) Fura-2FF- and FluoZin-3-loaded neurons incubated in a Ca2+-free and Zn2+-free Locke’s buffer containing 158 mM Na+ and supplemented with 100 μM EGTA (EGTA). Where indicated, 5 μM gramicidin (Gramic) was applied to permeabilize the plasma membrane to H+, Na+ and K+; to induce pHi drop, extracellular pH was decreased to 6.0; TPEN (10 μM) was added to chelate Zn2+. Left and right panels show Fura-2FF and FluoZin-3 data, respectively, simultaneously monitored in 32 neurons. In three neurons (red) unlike in other neurons (green), the Fura-2FF signal failed to drop upon TPEN application. (b) Average FluoZin-3 ± SE data from all cells shown in (a). At the end of this experiment, the maximal FluoZin-3 signal (Fmax) was measured at a pH of 6.0 (Zn pH 6.0) and a pH of 7.4 (Zn pH 7.4). Note that the pH change failed to affect Fmax. The values listed in the box are discussed in the text. (c) Analogous experiment to the one shown in (b) but without gramicidin. The data are averages ± SE from 24 neurons monitored in a single experiment. All experiments were repeated 5 times with similar results.