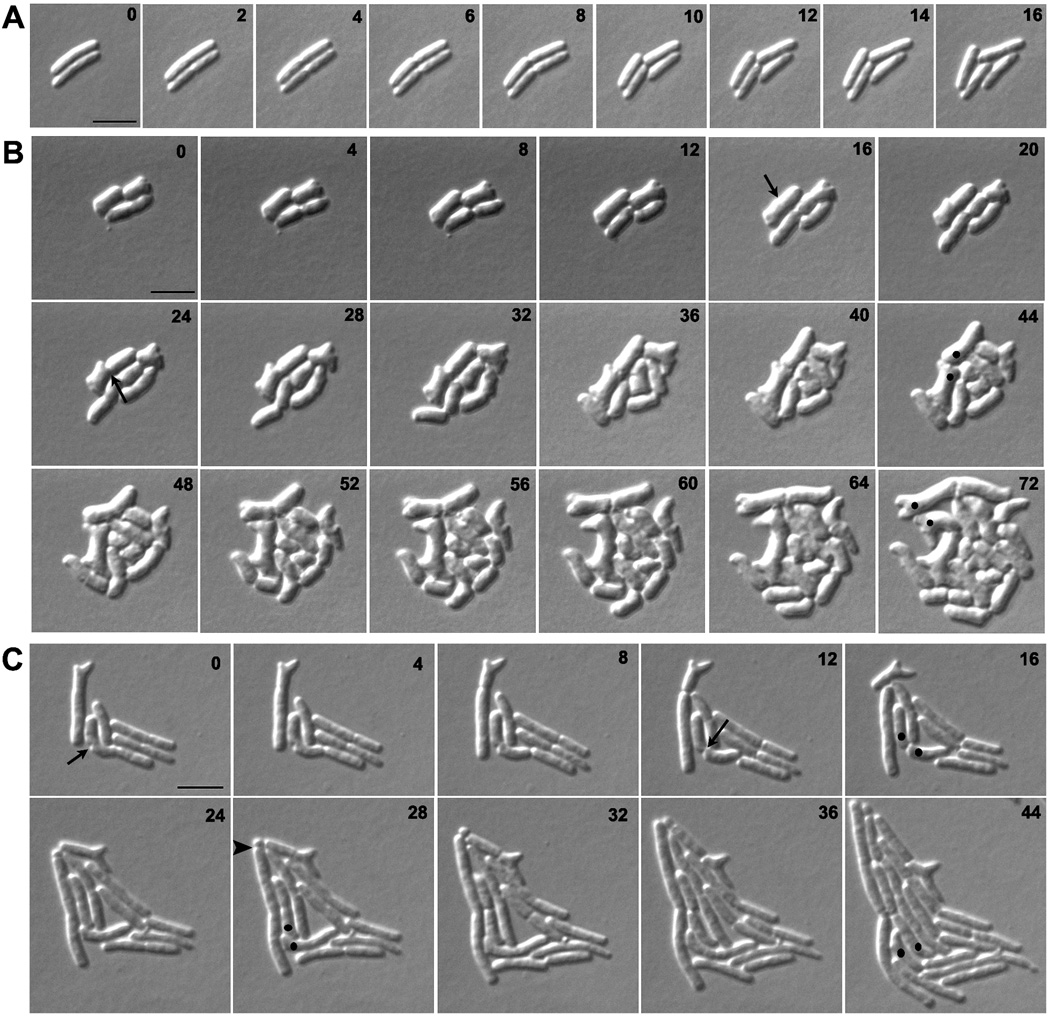
Fig. 2. Branches arise from abnormal septation.
E. coli strains A) CS109 (wild type), B) CS612-1 (Δ PBPs 4, 5, 6, 7, AmpC and AmpH), and C) CS109 harboring pLPZ, were grown and imaged as described in Experimental Procedures. Arrows in panels B and C represent abnormal cell constrictions. In panels B and C, dots were used to follow abnormal cell poles produced by abnormal cell constrictions and which gave rise to branches. The arrow head in panel C marks a mini-cell. The numbers on each image indicates the time in minutes. The scale bar equals 5 µm.