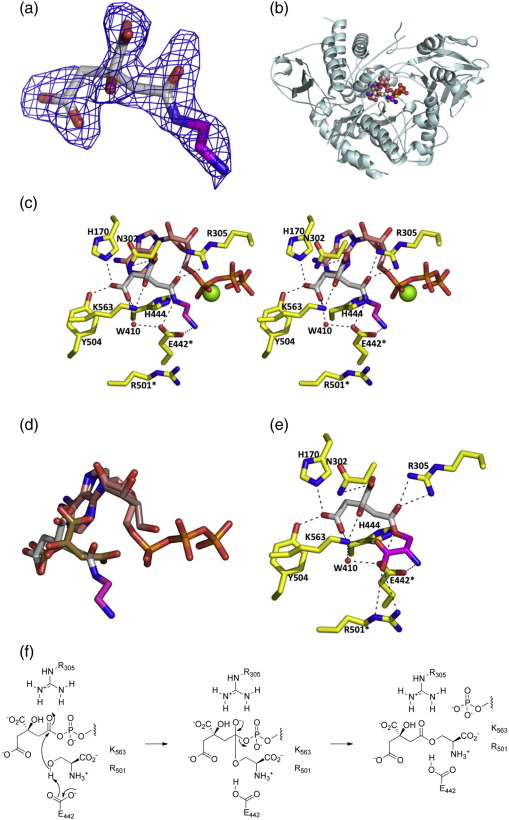
Fig. 3.
X-ray crystal structure of the AcsD/CEDA co-complex. (a) The Fo − Fc electron density map of CEDA at 2.5 σ with a carve radius of 2 Å. This map is derived from phases calculated before any ligand was added to the molecule. The final position of CEDA is shown as sticks with the carbon atoms of citrate colored white, the carbon atoms of ethylenediamine colored magenta, nitrogen atoms colored blue, and oxygen atoms colored red. (b) The protein backbone is shown as a ribbon with monomer B in cyan. CEDA is depicted in a space-filling representation, colored as in (a). ATP is also shown in a space-filling representation, with carbon atoms colored salmon, phosphorus atoms colored orange, and other atoms colored as in (a). Mg2+ is shown as a green sphere. (c) Interactions between CEDA and the protein. The side chains of key protein residues are shown in stick representation, with carbon atoms colored yellow and all other atoms colored as in (b). Residues that were mutated in this study are denoted by an asterisk (⁎). The H444 and R305 mutants were reported previously.20 (d) Superposition of the citrate/adenine (PDB code: 2WO3)20 and CEDA/ATP complexes of AcsD. The ligand positions are derived from superposition of the protein atoms. Citrate carbon atoms20 are colored olive, and adenine carbon atoms are colored light brown. CEDA carbon atoms are colored white (for those derived from citrate) and magenta (for those derived from ethylenediamine). ATP carbon atoms are colored salmon. The carboxyl group of citrate that undergoes adenylation and subsequent reaction with the hydroxyl group of l-serine changes position significantly in the structures. (e) A model of the O-citryl-l-serine complex (made by simple addition of a carboxylate group to the CEDA complex structure). The atoms of l-serine are colored magenta, and other atoms are colored as in (b). The carboxylate group of l-serine is proposed to be recognized by R501 and K563. (f) Proposed mechanism for the reaction of l-serine with the citryl adenylate catalyzed by AcsD.