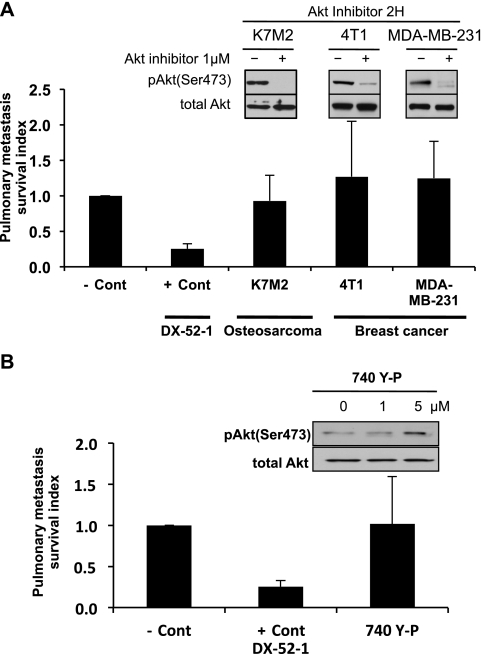
Figure 3.
Modulation of the Akt survival pathway does not change the early metastatic phenotype. (A) PuMA was performed using various GFP-labeled highly metastatic cell lines treated with 1 µM Akt inhibitor or vehicle for 4 days. The antitumor antibiotic 7-cyanoquinocarcinol (DX-52-1; + Cont), an agent that markedly affected cell survival in vitro and reduced metastatic cell numbers in PuMA, was used as a positive control for maximal inhibition of cell survival compared to the untreated negative control (- Cont). The inhibition of Akt phosphorylation (AktSer473), after 1 µM Akt inhibitor exposure, was confirmed by Western analysis. (B) PuMA was performed by injection of GFP-labeled low metastatic AS1.46 cells for 4 days. PuMA cultures with GFP-labeled low metastatic AS1.46 cells were treated with vehicle, PI3 kinase activator (740-Y-P), or DX-52-1. The activation of Akt pathway, after 740-Y-P exposure for 2 hours, was confirmed by Western analysis. Specificity of this activation was confirmed by the lack of ERK1/2 phosphorylation at the same exposures. Pulmonary metastasis survival index was calculated by dividing the tumor burden (total fluorescence area) in the Akt inhibitor-treated lung section by that of control-treated lung section. All data represent the mean values ± SD from experiments performed at least three times; one-way ANOVA.