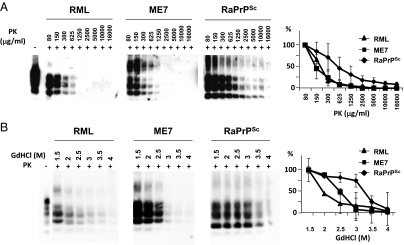
Fig. 3.
Proteinase K and guanidine denaturation studies using an in vivo rabbit prion strain. (A) De novo RaPrPSc inoculated rabbit brain homogenate was subjected to several different PK concentrations (80–16,000 μg/mL) at 42 °C for 1 h. ME7 and RML, two well-characterized prion strains, were used as reference. Although the mouse adapted scrapie strains showed a similar PK resistance, the rabbit prion strain showed a much higher resistance to PK treatment. (B) De novo RaPrPSc inoculated rabbit brain homogenate was denatured with different guanidine (GdHCl) concentrations (1.5–4 mol/L) and then subjected to standard Proteinase K (PK) digestion. ME7 and RML prion strains were used as reference. The rabbit prion showed a greater resistance to guanidine denaturation compared with RML and ME7, which had a low or intermediate resistance respectively. Graphs represent an evaluation of Western blots by densitometric analysis from three independent experiments (mean ± SE). All samples were analyzed by Western blot using monoclonal antibody D18.