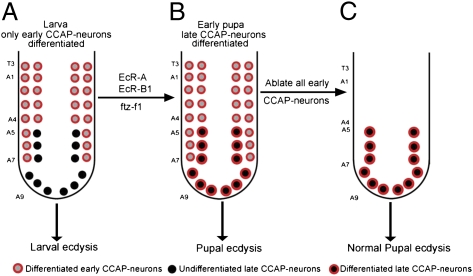
Fig. P1.
(A) In larvae, early CCAP neurons differentiate and participate in the regulation of the larval ecdysis process. (B) As the pupa forms, inductive signaling mediated through ecdysone receptors A and B1 (EcR-A/B1) and ftz-f1 triggers differentiation of late CCAP neurons to express appropriate peptide hormones and project their axons out of the central nervous system. (C) Previous work has shown that targeted ablation of every CCAP neuron blocks pupal ecdysis (2). However, we found that similar ablation of all of the early CCAP neurons, leaving only the late CCAP neurons intact, allows pupal ecdysis to proceed normally. This result shows that late CCAP neurons play a key role in this behavior.