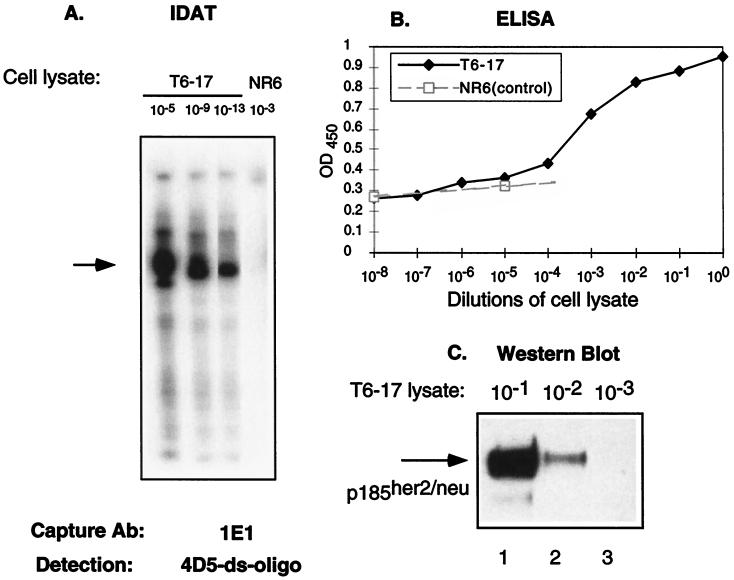
Figure 1.
A comparison of the sensitivity of several assays. (A) IDAT assay in which lysates (1 mg/ml) from T6–17 or NR6 (p185her2/neu negative) cells were diluted as indicated and captured by the anti-p185her2/neu Ab 1E1. The ds-oligo-conjugated mAb 4D5 was used to detect the antigen and perform the amplification assay. Although we detected a positive band in T6–19 cells at 10−13 dilution, no positive band was noticeable in the control NR6 cells at 10−3 dilution. It should be noted that this type of RNA amplification can lead to smaller-sized signals because of premature T7 termination and RNA degradation. Such smaller-sized signals are apparent in some figures. (B) A conventional sandwich ELISA assay with 1E1 and 4D5 was performed on cell lysates. An anti-human IgG-horseradish peroxidase (Zymed) was used as the secondary Ab. Results from NR6 cell lysates also were included to show the baseline of the ELISA assay. The ELISA assay detects p185her2/neu readily only at 10−4, 10−3, 10−2, 10−1, and 100 dilutions. (C) Western blot assay. T6–17 cell lysate (lane 1, 10 μl; lane 2, 1 μl; lane 3, 0.1 μl, equal to 10−1, 10−2, and 10−3 dilutions, respectively, as in A and B) were loaded for 6% PAGE. A polyclonal anti-p185her2/neu Ab NEU from Santa Cruz (200 μg/ml) was used for Western blot at 1:2,000 dilution.