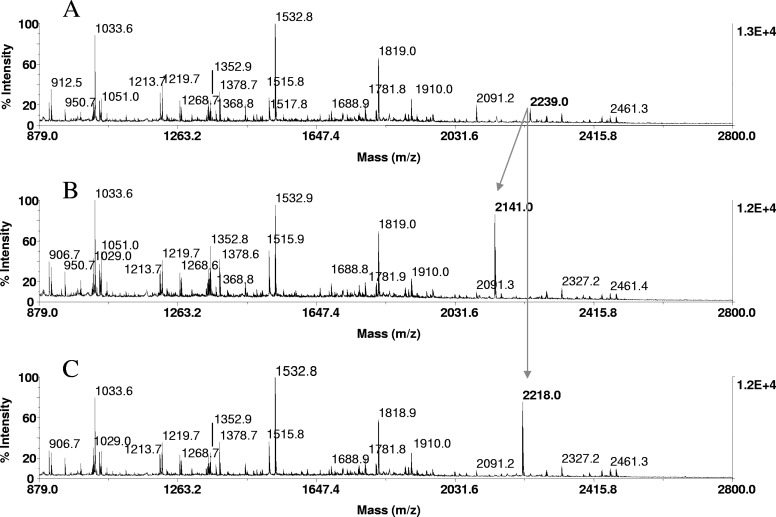
FIGURE 6.
Phosphopeptide identification in proteolytic digests of α-catenin, immunoprecipitated from EGF-stimulated A431 cells. Tryptic in-gel digests of α-catenin, derived from 20 pmoles protein loaded onto the gels, were bound to ZipTipC18 pipette tips and subjected to β-elimination and β-elimination with concurrent Michael addition under conditions described in Fig. 1. One-tenth of the eluates corresponding to ∼2 pmoles digests was applied to the target. MALDI-TOF spectra of (A) untreated tryptic digest, (B) after β-elimination, and (C) after β-elimination with concurrent Michael addition. Cross arrows indicate a phosphopeptide at m/z 2239.0, its β-elimination product at m/z 2141.0, and its thioladduct at m/z 2218.0. The diagnostic mass signature of 21 Da, accompanying the reactions, identified the peptide at m/z 2239.0 as the monophosphorylated species recognized as a phosphoseryl peptide, as it reacted under conditions that selectively promote phosphoserine conversion. The peptide mass-matched to a tryptic fragment within the known protein sequence (TPEELDDpSDFETEDFDVR), spanning residues 634–651. As indicated in bold, the sole serine at position 641 was tentatively assigned as the site of phosphorylation. This sequence-dependent assignment was subsequently confirmed by MALDI-TOF/TOF and LC-MS/MS.