FIGURE 7.
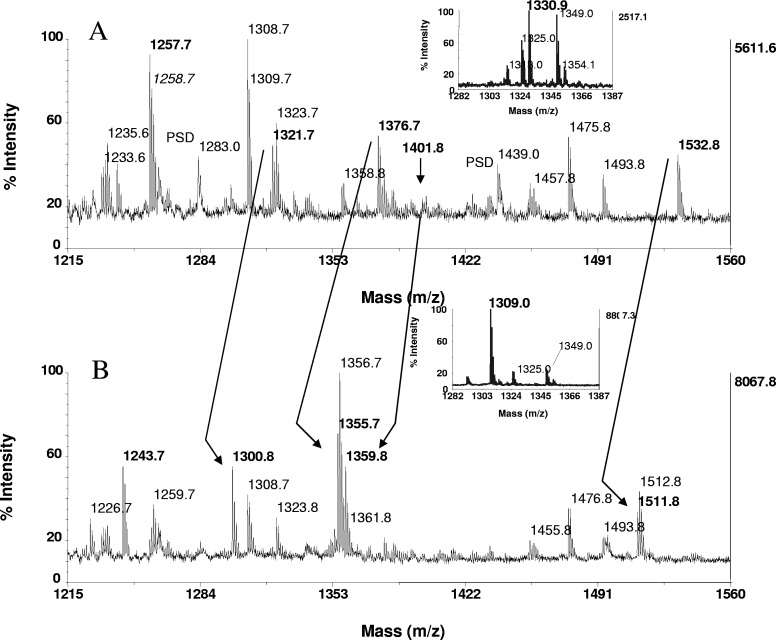
Phosphopeptide identification in proteolytic digests of Maf1. Tryptic and peptic in-gel digests of Maf1, derived from 15 pmoles protein, loaded onto the gels, were bound to ZipTipC18 pipette tips and subjected to β-elimination with concurrent Michael addition under the conditions described in Fig. 1. Expanded section of the MALDI-TOF spectra of (A) untreated tryptic digest and (B) after β-elimination with concurrent Michael addition. Arrows across the spectra indicate fragments recognized as phosphorylated by the characteristic mass shift of 21 Da/phosphoamino acid. Note the prominent ion of the thiol adduct at m/z 1359.8, recognized as a doubly phosphorylated species, undetectable in A (arrow) and mass-matched to RRpSpSSSSISSFK (residues 175–185). The known and assigned phosphorylation sites at serine 177 and 178, respectively, are marked in bold in the sequence. The ion at m/z 1321.7 corresponds to the singly phosphorylated form of the peptide. Additional ions identified in A were derived from monophosphorylated species and include the fragments at m/z 1376.7 and m/z 1532.8, corresponding to the sequences RDpSNSFWEQK (residues 88–97) and RDpSNSFWEQKR (88–98), in which, serine 90 was assigned by MS/MS as the site of phosphorylation. The peptide in A at m/z 1257.7 was identified as a carbamidomethylated species by the mass shift of 14 Da and mass-matched to VAYLYLICSR (residues 333–342) in the known protein sequence. Expanded section of the MALDI-TOF spectra of (A, inset) untreated peptic digest and (B, inset) after β-elimination with concurrent Michael addition. The peptic fragment at m/z 1330.0 was identified as a monophosphorylated species mass-matched to WEQKRRIpSF (residues 94–102) and hence, assigns serine in position 101 as a novel site of phosphorylation. One-tenth of the eluates of both digests, corresponding to ∼1.5 pmoles digest, was consumed for MALDI-TOF analysis.