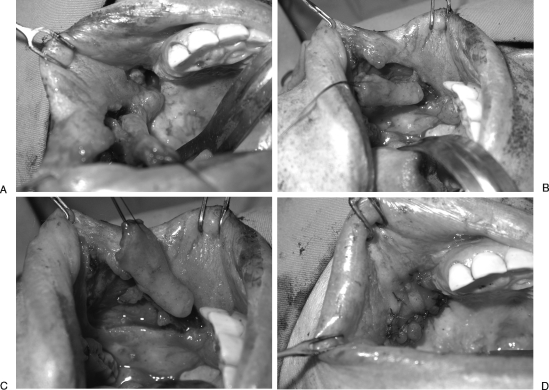
Figure 2.
Oro-antral fistula reconstructed with local rotation flap for antral lining and facial artery musculomucosal (FAMM) flap for oral lining. The patient is a 43-year-old woman who had previously undergone a right partial maxillectomy and reconstruction. Attempted closure had been performed on three occasions without success. (A) View from below demonstrating the presence of an oro-antral fistula. The FAMM flap has been elevated. (B) After marking the course of the facial artery with a hand-held Doppler, the FAMM flap is marked, with the facial artery in the center of the flap. As the FAMM flap in this case is used to reconstruct a defect in the maxillary region, the flap is pedicled on the blood supply coming from the superior aspect of the flap. The inferior incision is performed first, and the facial artery and vein are located and ligated. After gentle tugging on the vessels, the surgeon can confirm the location of the vessels and re-mark if necessary. The flap is elevated from distal to proximal below the plane of the vessels. (C) FAMM flap after complete isolation of the pedicle and elevation. (D) Local random pattern flaps were used to line the antral side of the defect. The FAMM flap is inset into the defect and used to obliterate the dead space and line the oral side of the fistula.