Figure 2.
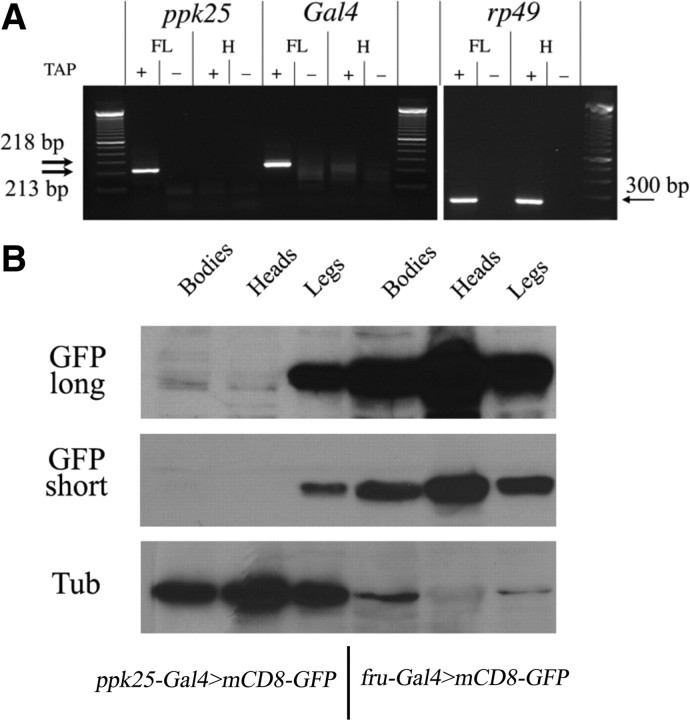
Both ppk25-Gal4 and the endogenous ppk25 gene are expressed in legs but not heads. A, Transcripts of the ppk25-Gal4 transgene and of the endogenous ppk25 gene initiate at the same nucleotide, and are found in front legs but not in heads. RNA extracted from front legs (FL) or heads without antennae (H) was analyzed by amplification of cDNAs using RLM RACE, which only amplifies cDNAs produced by reverse transcription of 5′-capped RNAs (Schaefer, 1995). + and − indicate whether the RNA sample was treated with tobacco acid pyrophosphatase (TAP) to generate a 5′ monophosphate required for ligation to the RNA adaptor. Specific antisense primers were used for ppk25, Gal4, and rp49. The unique bands of 218 and 213 bp observed in cDNAs from front leg and resulting from amplification of the ppk25 and Gal4 transcripts, respectively, were sequenced, confirming the reported start site for the ppk25 mRNA (Ben-Shahar et al., 2007), and an identical start site for the ppk25-Gal4 transgene (Fig. 1). In contrast, the ubiquitous rp49 mRNA yields a predicted band of 300 bp that is detected equally by RLM-RACE using cDNA from front legs and heads. B, Expression of GFP under control of ppk25-Gal4 is detectable in legs but not heads or bodies. Extracts were made from bodies (without legs, wings, or heads), heads (without antennae), or legs of males expressing mCD8-GFP under control of either ppk25-Gal4 or fru-Gal4 (Stockinger et al., 2005) as indicated, and analyzed by immunoblotting with anti-GFP. The blots were then stripped and reprobed with anti-tubulin antibody (Tub), showing that for males containing the ppk25-Gal4 driver, more extract from heads than legs was loaded on the gel. For those males, extracts from heads and bodies show no detectable GFP band above the background of nonspecific bands. GFP short and GFP long refer to different exposures of the same Western blot.