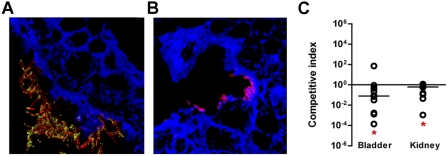
FIG 6 .
Role of FdeC in vivo in a model of ascending UTI. Confocal imaging analysis of FdeC expression in bladder from mice independently infected with UPEC wild-type strain 536 (A) and the isogenic fdeC mutant strain (B). Tissue sections embedded in paraffin were stained with WGA conjugated with Alexa Fluor 647 (blue), while UPEC strain 536 was detected using a polyclonal serum raised against inactivated whole bacteria (red). FdeC was stained in green. The images are representative of multiple observations, from at least 10 sections. (C) Cochallenge experiments using the 536 wild-type strain and the fdeC isogenic knockout mutant. In vivo competitive indices (CI) were determined following cochallenge infections of female CBA/J mice with a 1:1 ratio of wild-type 536 and fdeC knockout mutant strains. At 48 h postinoculation, bacteria were enumerated by plating serial dilutions from tissue homogenates. The CI from each tissue was determined by dividing the mutant-to-wild-type ratio of CFU/g by the mutant-to-wild-type ratio of CFU from the mixed inoculum. Each dot represents bladders and kidneys from an individual animal. Bars indicate the median CI. Significant differences in colonization (*) (P values, <0.05) were determined by the Wilcoxon signed rank test. A CI of <1 indicates a fitness defect.