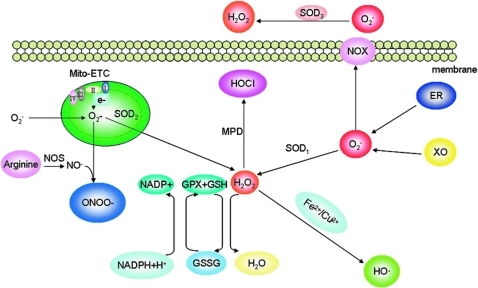
FIG. 1.
Cells maintain redox homeostasis through a balance of generation and elimination of reactive oxygen species (ROS). Superoxide (O2−), the principal form of ROS, comes from the byproducts of electron leakage of mitochondrial electron transport chain (Mito-ETC), endoplasmic reticulum (ER), and membrane-located NAD(P)H oxidase complex (NOX). O2− can be rapidly converted to hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) by superoxide dismutase (SOD); H2O2 can be catalyzed to release hydroxyl radicals (HO•) in the presence of Fe2+ or Cu2+ ions. H2O2 can be converted by myeloperoxidase (MPD) to hypochlorous acid (HOCl), a stronger oxidant. H2O2 is converted to H2O+O2 by catalase or glutathione peroxidase (GPX). Nitric oxide (NO•), once generated from arginine catalyzed by nitric oxide synthase (NOS), is rapidly converted to peroxynitrite (ONOO−) by reacting with O2−. (To see this illustration in color the reader is referred to the web version of this article at www.liebertonline.com/ars).