Table 1.
Redox Modifications That May Influence Mitochondrial Function Directly or Indirectly
| Biological function and target protein(s) | Redox modification | Consequence/mitochondrial effect |
|---|---|---|
| Energetics | ||
| Complex I | S-SG | Either increases activity/decreases 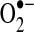 , or decreases activity/increases , or decreases activity/increases 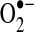
|
| S-NO; acetylation | Decreases activity/increases or decreases 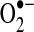
|
|
| Complex II | Acetylation | Inhibitory |
| Complex IV | Cys-oxidation/S-NO | Inhibitory |
| ATPase | S-NO | Inhibitory |
| TCA enzymes | ||
| Aconitase/α-KGDH | S-SG/Cys-oxidation | Inhibitory |
| ICDH | Acetylation | Inhibitory |
| MDH | Acetylation | Activating |
| Mitochondrial transporters | ||
| ANT | S-S; S-NO | Modulates ADP transport/MPT and cell death |
| VDAC | Cys oxidation | Possible role in apoptosis |
| UCP | S-SG | Maintains inactive state |
| Antioxidant enzymes | ||
| GPx-1 | Se-oxidation | Loss of Se, inhibitory |
| Se-NO | Inhibitory | |
| Grx1 | S-S; Cys-NO | Inhibitory |
| Grx2 | Oxidation | Loss of [Fe-S] group releases active monomers |
| GR | S-NO; S-OH; S-O2H | Inhibitory |
| Trx | S-S | Releases ASK1 to activate JNK-mediated apoptosis |
| Prx | Cys-oxidation (S-S; S-OH; S-O2H; S-O3H) | Inhibitory |
| Mitochondrial networks | ||
| Drp1 | S-NO | Possibly stimulates mitochondrial fission |
| Mitochondrial biogenesis | ||
| PGC-1α | Acetylation | Inhibitory |
| Apoptosis/autophagy | ||
| Caspase 3 | S-NO | Inhibitory; attenuates apoptotic signaling |
| BCL-2 | S-NO | Decreases proteasomal degradation of BCL-2; attenuates apoptosis |
| ATG4 | Cys-oxidation | Inhibits protease activity to promote autophagy |
| L-type Ca2+ channel | Cys-oxidation | Inhibitory, attenuates Ca2+-mediated apoptosis |
ANT, adenine nucleotide transporter; ASK1, apoptosis signal-regulated kinase 1; Cys, cysteine; Drp1, dynamin-related protein-1; Fe-S, iron–sulfur; GPx, glutathione peroxidase; GR, glutathione reductase; Grx, glutaredoxin; ICDH, isocitrate dehydrogenase; JNK, c-jun N-terminal kinase; MDH, malate dehydrogenase; MPT, mitochondrial permeability transition; 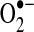 , superoxide anion; PGC-1, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ coactivator-1; Prx, peroxiredoxin; TCA, tricarboxylic acid; Trx, thioredoxin; UCP, uncoupling proteins; VDAC, voltage-dependent anion channel; α-KGDH, α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase.
, superoxide anion; PGC-1, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ coactivator-1; Prx, peroxiredoxin; TCA, tricarboxylic acid; Trx, thioredoxin; UCP, uncoupling proteins; VDAC, voltage-dependent anion channel; α-KGDH, α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase.
