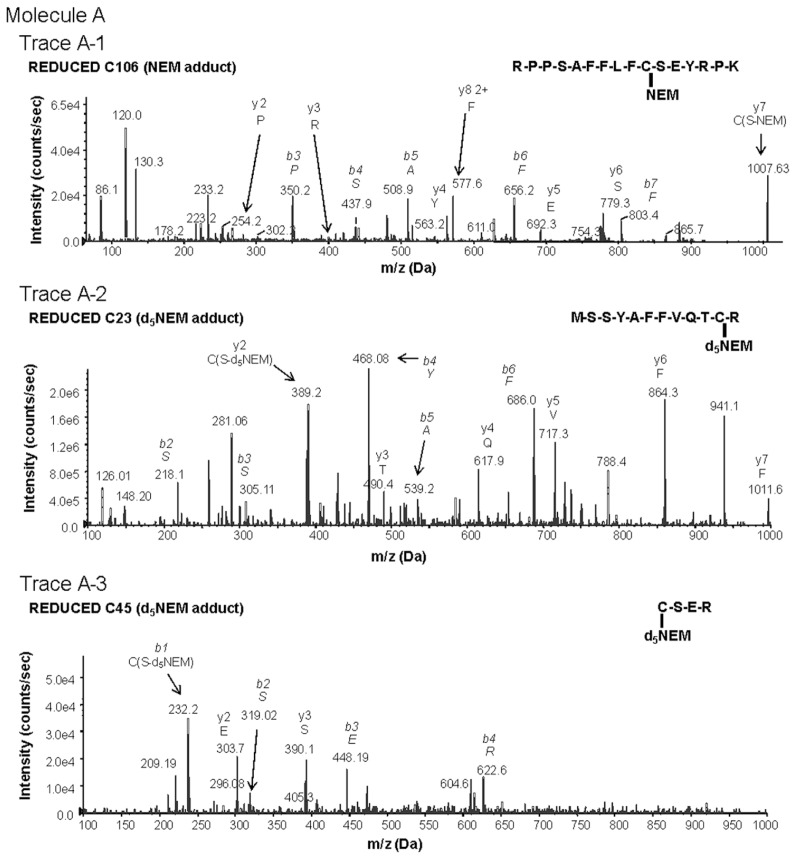
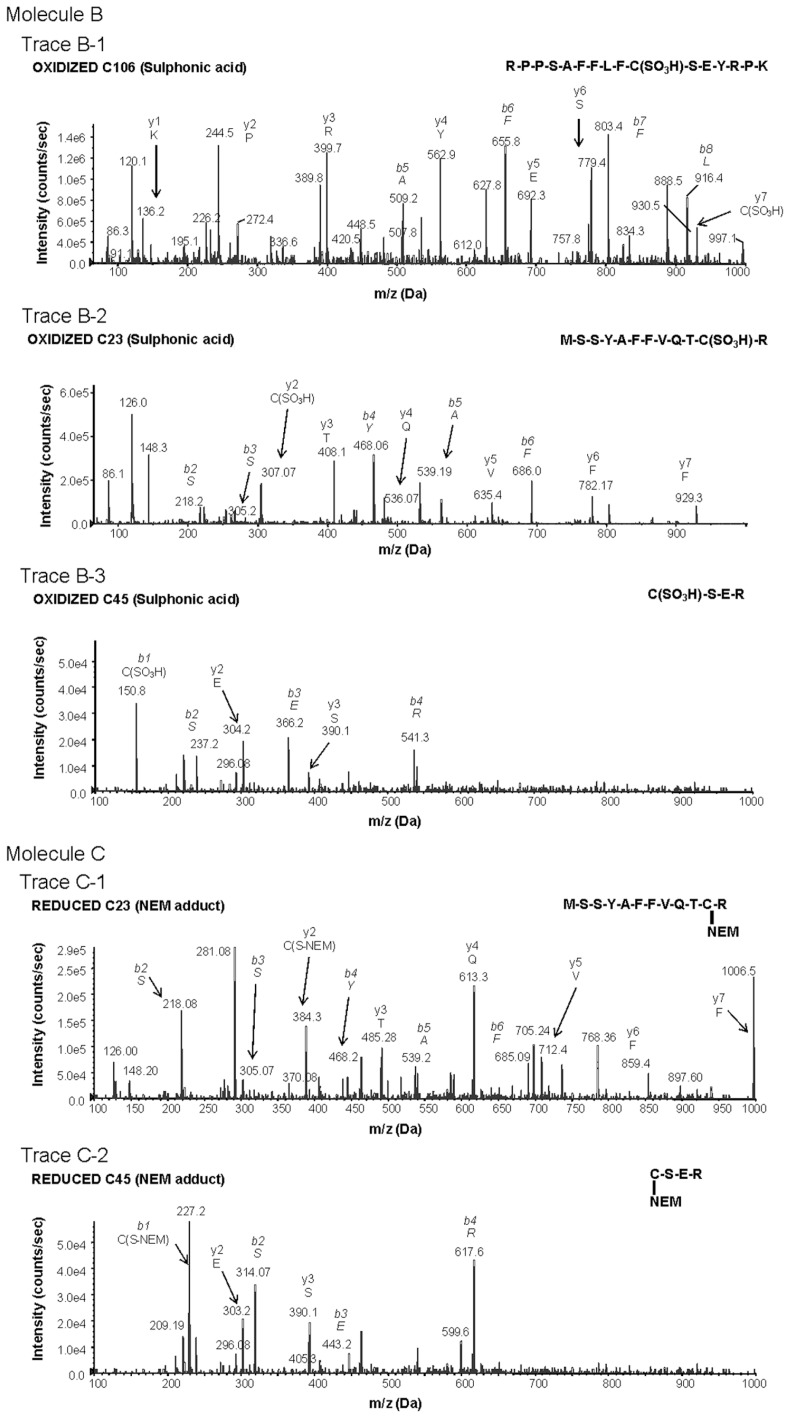
Figure 1.
Characterization of redox-dependent modifications of cysteine residues in HMGB1 using mass spectrometry. Molecule A: mass spectrometric characterization of molecule A on C106 (A-1), C23 (A-2) and C45 (A-3). A-1: Peptide-containing HMGB1 amino acids 97–112 with a thiol capped NEM adduct indicating reduced C106. A-2: Peptide-containing HMGB1 amino acids 13–24 following DTT reduction of a disulfide bond and subsequent adduction of C23 with d5NEM. A-3: Peptide-containing HMGB1 amino acids 45–48 following DTT reduction of a disulfide bond and subsequent adduction of C45 with d5NEM. Molecule B: mass spectrometric characterization of molecule B on C106 (B-1), C23 (B-2) and C45 (B-3). B-1: Peptide-containing HMGB1 amino acids 97–112 containing a C106 as a sulphonic acid. B-2: Peptide-containing HMGB1 amino acids 13–24 containing a C23 as a sulphonic acid. B-3: Peptide-containing HMGB1 amino acids 45–48 containing a C45 as a sulphonic acid. Molecule C: mass spectrometric characterization of molecule C on C23 (C-1) and C45 (C-2). C-1: Mass spectrometric characterization of C23. Peptide-containing HMGB1 amino acids 13–24 with a thiol-capped NEM adduct indicating reduced C23. C-2: Peptide-containing HMGB1 amino acids 45–48 with a thiol-capped NEM adduct indicating reduced C45. Peptide sequences and b and y ions are indicated on each trace as required. MS/MS traces are representative of three independent investigations.