Figure 1.
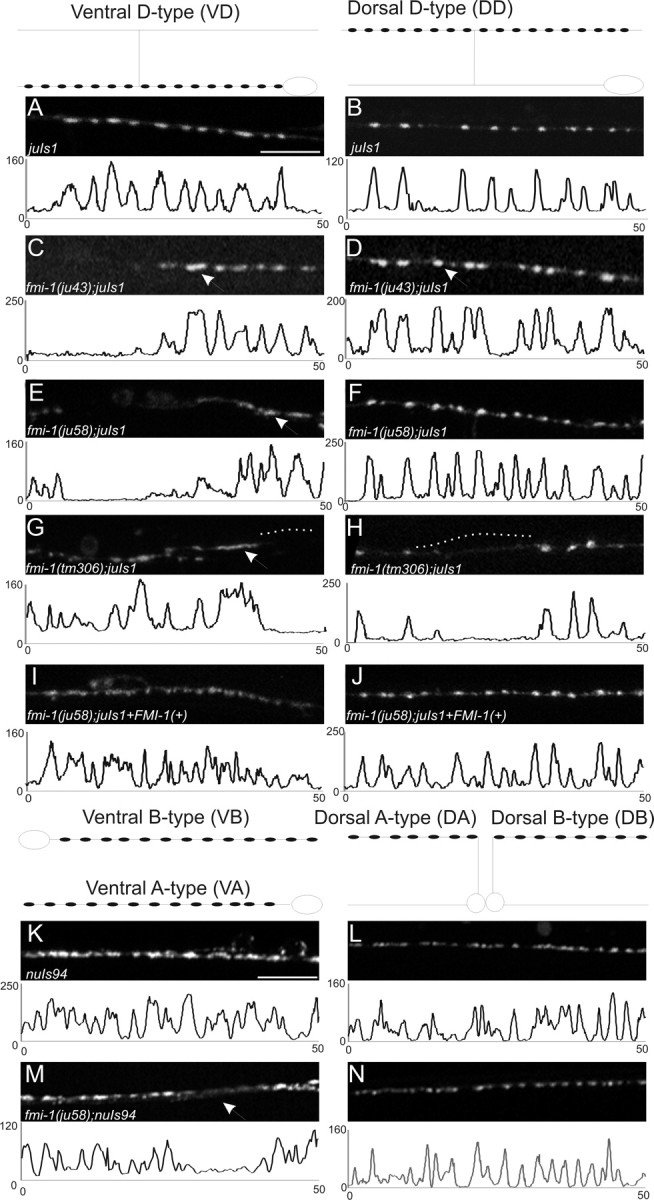
GABAergic NMJs are malformed in fmi-1 mutants. GABAergic (A–J) and cholinergic (K–N) NMJs were examined using SNB-1::GFP to visualize synaptic vesicle clusters. The shape of the VD and DD motorneurons is depicted above A and B, respectively, and the location of the synapses within those cells is illustrated (black circles). In all panels, left is anterior. A–J, Images are a 50 μm section of the ventral (A, C, E, G, I) or dorsal (B, D, F, H, J) nerve cords, and below each image is a plot profile for each image to demonstrate the approximately similar-sized puncta in wild-type and how they are divergent in fmi-1 mutants. Wild-type animals (A, B) had consistently sized puncta that were evenly spaced along the nerve cords. C–H, In the GABAergic motorneurons of fmi-1 mutants, we observed larger synapses (C, D, arrows) and misshapened (E, G, arrows) puncta. Frequently, there were long regions of the nerve cord lacking synapses (gaps) (G, H, dotted lines). I, J, We partially rescued the ju58 defects using a fosmid containing fmi-1. These animals had a significant reduction in synaptic size relative to ju58 alone, and fewer long gaps lacking GFP were found in the nerve cords. K–N, SNB-1::GFP expressed in the cholinergic neurons appear less defective than in the GABAergic neurons. Schematics of the shape and location of synapses within these neurons are shown above K and L. Note that the VA and VB synapses, as well as those in the DA and DB neurons, would overlap in vivo, which is not illustrated here for simplicity. In wild-type animals, SNB-1::GFP puncta were normally sized and tightly clustered. M, N, In the fmi-1(ju58) animals, the puncta were approximately the same size, although we observed a few gaps where puncta are weaker or absent (M, arrow). Scale bars, 10 μm.
