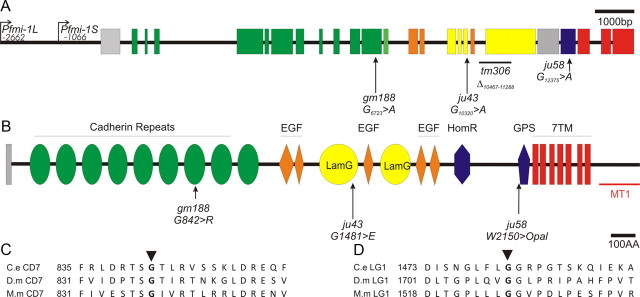
Figure 2.
Lesions identified in the fmi-1 gene and protein. A, Schematic presentation of the fmi-1 gene and locations of lesions. Nucleotide numbering is with respect to the start of translation. The promoter regions used for GFP expression (Pfmi-1L) and the segment present in the rescuing fosmid (Pfmi-1S) are indicated. Exons and their corresponding protein domains are color coded. B, The FMI-1 protein structure was determined using SMART (Simple Modular Architecture Research Tool). The extracellular region of the protein is predicted to have nine cadherin repeats (green ovals), five EGF-like domains (orange diamonds), two LamG domains (yellow ovals), as well as a hormone receptor-related domain (HormR; blue hexagon) and a proteolytic cleavage site that is present in G-coupled protein receptors, e.g., latrophilins [G-protein-coupled receptor proteolytic site domain (GPS); blue pentagon]. FMI-1 has seven predicted transmembrane domains and an intracellular domain of ∼142 amino acids. C, The gm188 mutation in the seventh Cadherin repeat affects a highly conserved glycine residue [alignment of C. elegans (C.e.) FMI-1, Drosophila (D.m.) Flamingo, and M. musculus (M.m.) Celsr2]. D, Partial alignment of the first LamG domain showing the glycine affected by ju43.