Figure 3.
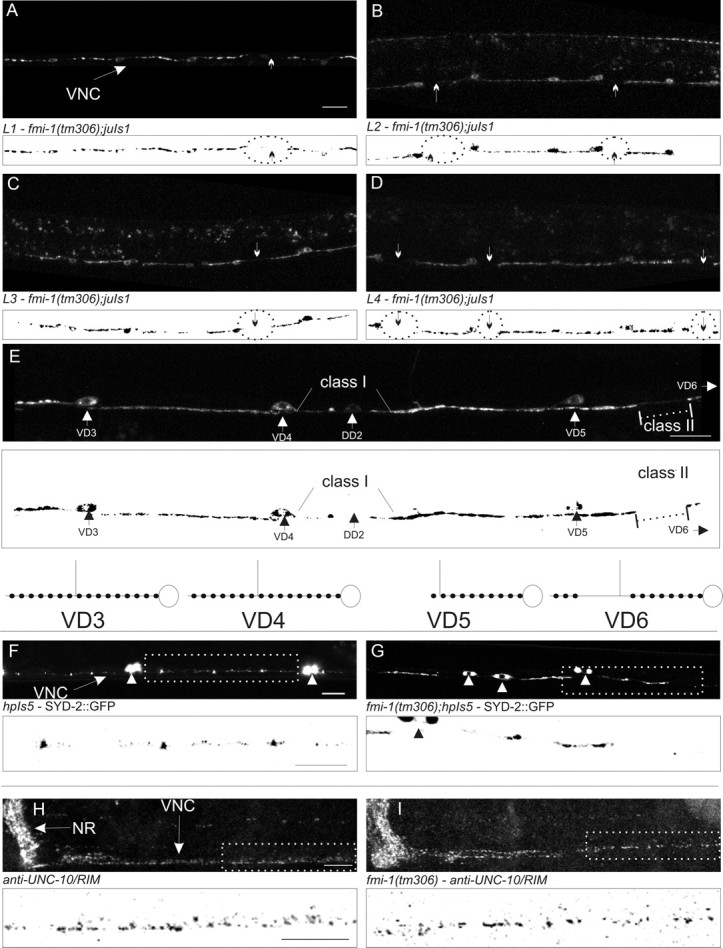
FMI-1 causes synaptic defects during development. A–D, GABAergic neurons in the ventral nerve cord (VNC) in tm306;juIs1 (Punc-25::SNB-1::GFP) were imaged at each larval stage (L1–L4). Regions lacking SNB-1::GFP (circles and arrows) were present in all stages examined. Below each panel is a thresholded mask of the image (black/white inverted). E, An adult animal with both class I and class II gaps is shown. VD5 appears to have a class I gap because the gap extends from end of the synaptic puncta (large arrowhead) to the point of VD4. The small amount of fluorescent material in that region seems to come from the DD2, which is more weakly fluorescent. In comparison, the puncta formed in VD4 extend all the way to VD3. VD6 (cell body not shown) has a class II gap (dotted line) because VD6 forms puncta distal to the gap before VD5. A diagram illustrating these cells is drawn above and to the right. F, G, SYD-2::GFP accumulates in small puncta in the nerve cord (F, arrow) and motorneuron cell bodies (F, G, arrowheads). In fmi-1 mutants (G), SYD-2::GFP is clustered in larger puncta with bigger gaps between puncta. H, I, UNC-10 localized to discretely sized and spaced puncta in the nerve ring (NR) and VNC. I, UNC-10 localization was grossly wild type in fmi-1(tm306). Boxed regions in F–I are depicted with a black/white inverted image below each panel. Scale bars, 10 μm.
