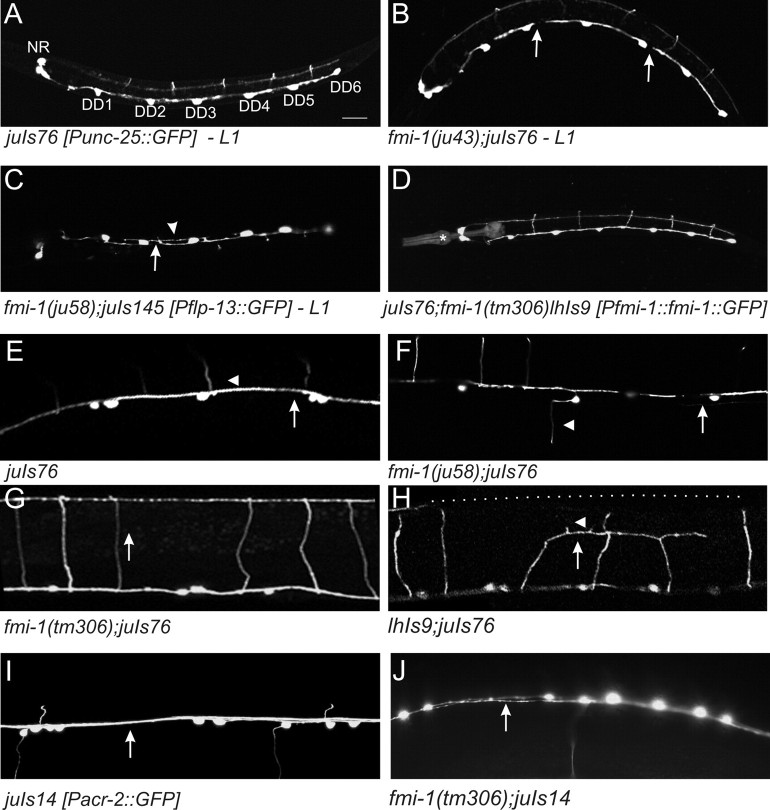
Figure 5.
Axon guidance defects in fmi-1. GABAergic and cholinergic motorneurons were visualized using GFP reporters juIs76-Punc-25::GFP (A, B, D–H), juIs145-Pflp-13::GFP (C), and juIs14-Pacr-2::GFP DA, DB, VA, and VB (I, J). A–D, The six DD motorneurons are the only GABAergic motorneurons present during L1s [VDs form at the end of the L1 stage; 4 RME neurons are in the nerve ring region (NR)]. The process of each neuron extends anteriorly to the next cell body, i.e., DD3 extends to DD2. B, C, DDs in the fmi-1 mutants often exhibit incomplete axon extension (arrows). C, DD axons often defasciculated into two nerve bundles (arrowhead). D, DD axon extension defects were rescued by FMI-1::GFP using its endogenous promoter (lhIs9, *Pmyo-2::RFP, which is the coinjection marker). E, In wild type, GABAergic axons form as a single contiguous fascicle in the ventral cord (arrow). Commissures (arrowhead) posterior to DD1 and VD1 grow toward the right side, which is up in this ventral view. F, In fmi-1 mutants, GABAergic motorneurons exited the ventral cord on the incorrect side and often had defects in the extension of the axons (arrow). The gap is likely attributable to the premature termination of both the VD and DD axons. G, In wild-type animals (not shown) and fmi-1(tm306), commissures extend along the dorsoventral axis (indicated by arrow) fully to the dorsal cord. H, Overexpression of FMI-1::GFP (lhIs9) caused aberrant guidance and premature turning and termination of GABAergic commissures (arrow), with some having ectopic neurites (arrowhead). The position of the dorsal cord is indicated by the dotted line. I, Cholinergic processes within the ventral cord (arrow) appear as a single, cohesive fascicle in wild-type animals. J, In the ju58 animals, cholinergic axons of defasciculated (arrow). Scale bar, 10 μm.