Figure 9.
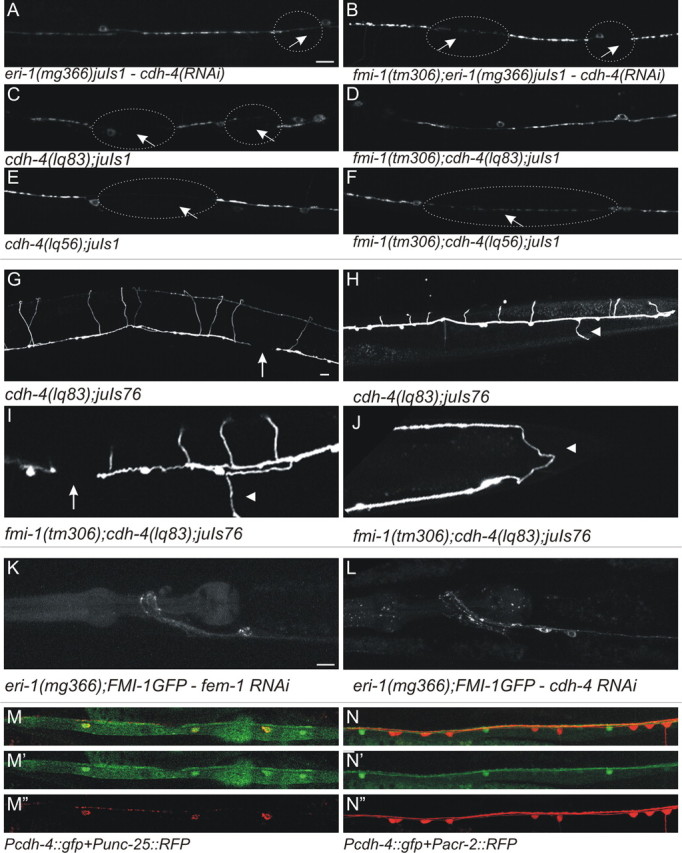
fmi-1 and cdh-4 mutations cause similar phenotypes in VD patterning. A, The eri-1(mg366)juIs1 animals treated with cdh-4 RNAi had elongated SNB-1::GFP puncta interrupted by large gaps (circles and arrows). B, The cdh-4 RNAi caused no enhancement of the phenotype present in eri-1(mg366)juIs1;fmi-1(tm306) animals. C–F, The cdh-4 loss-of-function mutations, lq83 (C, D) and lq56 (E, F), caused fmi-1-like phenotypes, but neither enhanced defects present in fmi-1(tm306). G–J, The cdh-4(lq83) caused GABAergic axon pathfinding defects, including axon extension failure (G, I, arrows) and left/right defects (H, I, arrowheads). I, J, Animals lacking both cdh-4 and fmi-1 have pathfinding defects that are similar to the single mutants. J, In this animal, the VD13 axon (arrowhead) is extended toward the posterior rather than the anterior. K, L, The cdh-4(RNAi) does not grossly disrupt FMI-1::GFP localization relative to control, fem-1(RNAi). M, N, In larva and adults, Pcdh-4::gfp (hdIs46) expression overlaps with a marker for the GABAergic neurons (red, Punc-25::rfp; M) but not the cholinergic neurons (red, Pacr-2::rfp; N). Scale bars, 10 μm.
