Figure 10.
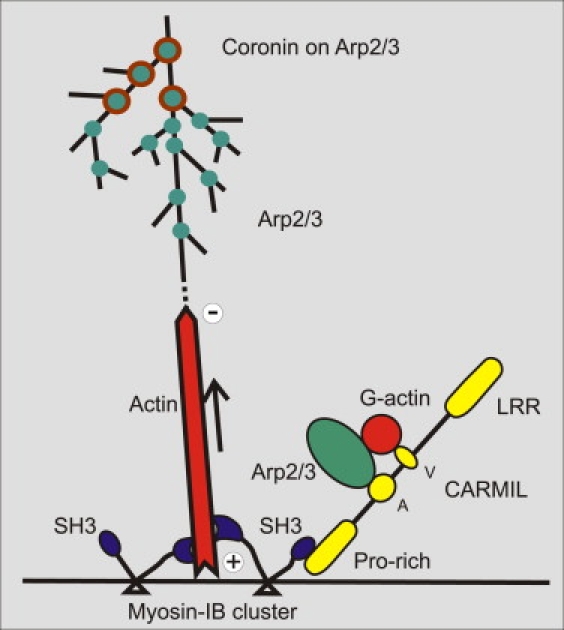
Hypothetical role of MyoB in organizing actin filaments into waves and in recruiting the Arp2/3 complex. Based on the z-scans shown in Fig. 9A, MyoB (blue) is proposed to assist by multiple interactions in organizing the membrane-anchored actin network. MyoB binds with its tail (triangles) to the plasma membrane (42), and its N-terminal motor domain moves toward the plus end of actin filaments. In that way, clusters of MyoB may keep the growing filaments separate from the membrane (arrow), thus allowing subunits to enter. The C-terminal SH3 domain of MyoB interacts with the proline-rich region of the adaptor protein CARMIL (yellow), which links MyoB to the Arp2/3 complex through its acidic domain (A). These interactions of CARMIL as well as the presence of the protein-protein interacting, verprolin-like (V), and leucine-rich-repeat (LRR) sequences are adopted from Jung et al. (13). The actin filaments are branched at sites of Arp2/3 binding (green) until activity of the Arp2/3 complex is inhibited by coronin (brown circles).
