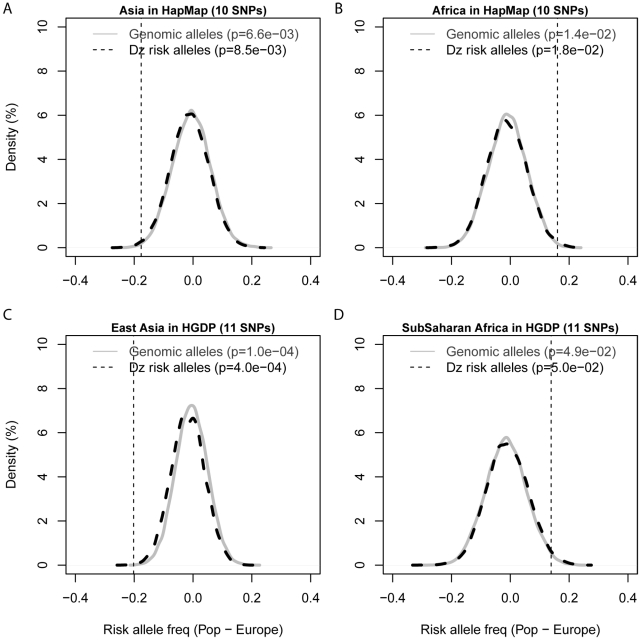
Figure 3. An ensemble of T2D risk alleles demonstrates significant directional differentiation of frequencies among human populations, compared to genomic control alleles and risk alleles for other diseases.
Eleven independent cross-ethnic T2D risk alleles were combined as an ensemble to calculate the average increased frequencies in the populations in Asia (A) and Africa (B) from HapMap, and the East Asia (C) and Sub-Saharan Africa (D) from HGDP, compared with the frequencies in the European populations. The average increased RAFs of T2D risk alleles are shown as dotted vertical lines, and compared against the null distributions of average increased RAFs of 11 alleles randomly drawn from genomic alleles (solid black curve) and disease-susceptible risk alleles (dashed grey curve) that share the same allele frequencies with T2D risk alleles in the European populations. Two-side p values were calculated by comparing dotted vertical lines against the null distributions of frequency-matched control genomic alleles and risk alleles of other diseases. SNPs used in each figure were summarized in Table S4.