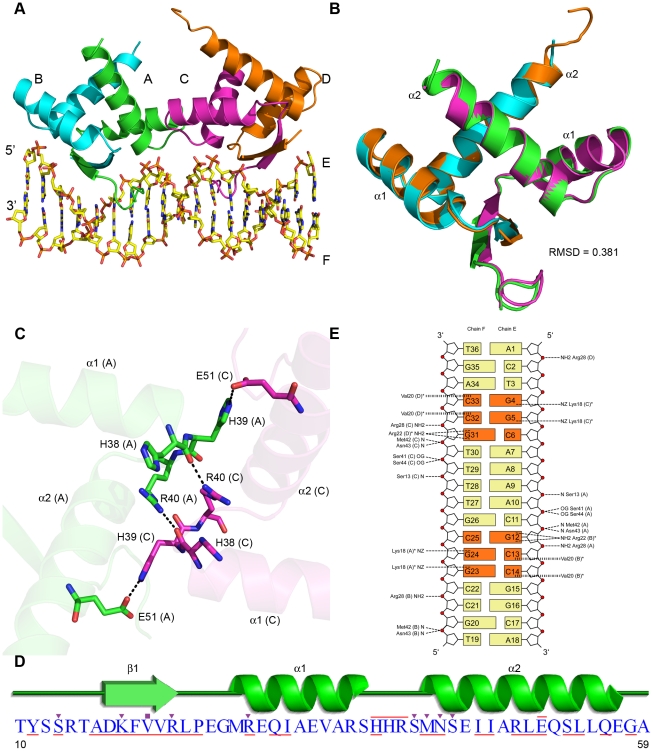
Figure 1. Structural overview of AmrZ - amrZ1 complex.
(A) The Δ42 AmrZ protein binds to the 18 bp amrZ1 binding site as a dimer of dimers. One dimer is composed of chains A and B (green/cyan), while the other dimer is composed of chains C and D (magenta/orange). (B) The superposition of AmrZ dimers show no major structural differences between them (Cα RMSD = 0.381 Å). (C) The dimer - dimer interface is created by a network of hydrogen bonds between the residues in the loop region between α-helix 1 and α-helix 2 of chains A and C. (D) Secondary structure representation of one AmrZ ribbon-helix-helix monomer. Residues forming hydrogen bonds to DNA are indicated by the purple triangles, while residues forming hydrophobic interactions to DNA are indicated by purple squares. Residues forming the dimer interface between each monomer are underlined in red, and the residues which form the dimer-dimer interface are overlined in red. (E) Schematic of both the sequence dependent and sequence independent interactions between AmrZ and amrZ1. Hydrogen bonding interactions to the DNA are illustrated with a short dashed line, while hydrophobic interactions are illustrated with a vertical dashed line. Nucleotides involved in sequence specific interactions are represented in orange. The peptide chain for each residue is labeled in parentheses, and residues that make contacts to more than one nucleotide are notated with an asterisk.