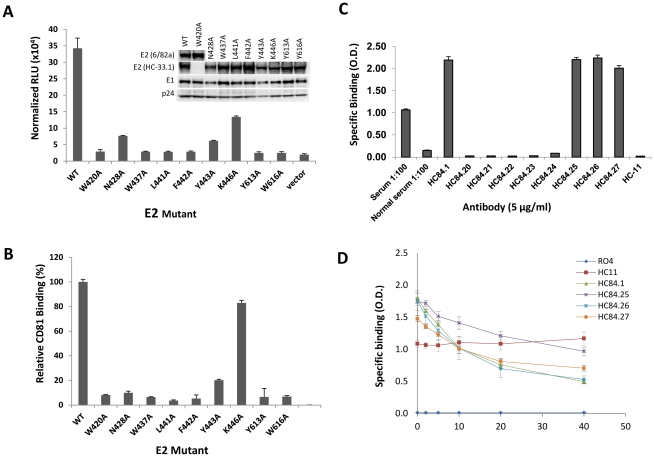
Figure 6. Effect of alanine substitution with each HC-84 contact residue on HCVpp entry, interaction with CD81, and HC-84 HMAb binding to “epitope-II".
(A) Wt and H77c HCVpp mutants, each bearing a single alanine substitution at a contact residue of HC-84 HMAbs, were produced, normalized by p24 as described in Materials and Methods, and employed to infect Huh7.5 cells. Virus entry was assessed by measuring luciferase activity on day 3 p.i. Results are shown as luciferase activity signals in infected cells, relative to signals from cells infected with vectors alone. Data are shown as the mean of three experiments ±SD, with each performed in triplicates. The inset shows incorporation of E1E2 glycoproteins into wt and mutant HCVpp that were partially purified by pelleting virus through a 20% sucrose cushion and followed by Western blot analysis. E2 in the majority of HCVpp mutants and wt were probed with HMAb HC-33.1, and in W420A HCVpp and wt, were re-probed with MAb 6/82a [29]. E1 was probed with HMAb H-111, an antibody to a linear E1 epitope [49]. HIV p24 was probed with an anti-HIV p24 antibody as a loading control. The images are composites. (B) Effect of each HC-84 contact residue on E2 binding to CD81. HC-84 epitope- related E2 mutant proteins were expressed in 293 T cells and captured in microtiter plates by GNA. Individual protein expression was normalized by binding of CBH-17, an HCV E2 HMAb to a linear epitope [18]. The wells were then incubated with CD81-LEL at 20 µg/ml. Detection of CD81-LEL captured by wt or mutated E2 was measured with anti-CD81 and shown as percent CD81 binding relative to wt. Data are derived from triplicate wells and shown as the mean of two experiments ± SD. (C) HC-84 HMAb binding to epitope-II by ELISA. Biotinylated-epitope II, aa434–446, was captured by streptavidin in microtiter wells. The wells were then incubated with each HC-84 HMAb at 10 µg/ml, serum (1∶100 dilution) from the individual whose B cells were employed to isolate the HC-84 antibodies, and a normal human serum (1∶100 dilution), as a negative control. Specific binding was detected by anti-human IgG-labeled horseradish peroxidase. (D) Peptide (epitope-II) inhibition of HC-84 antibody binding to E2. Recombinant H77C E1E2 lysate was captured by GNA in microtiter wells. The wells were then incubated with selected HC-84 HMAbs and two controls, HC-11 and R04 that were pre-incubated with epitope-II (labeled as peptide) at indicated concentrations. Binding was detected after anti-human IgG-labeled horseradish peroxidase. For C and D, the y-axis shows the mean optical density values for triplicate wells, the mean of two experiments ±SD.