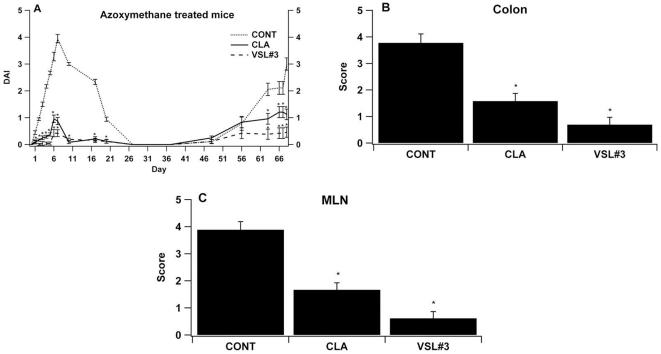
Figure 1. Effect of VSL#3 and dietary conjugated linoleic acid (CLA) supplementation on experimental azoxymethane-induced colorectal cancer.
C57BL/6J mice (n = 60) were treated with the VSL#3 probiotic (n = 20), CLA-supplemented (1 g/100 g) (n = 20) or control diets (n = 20) for 32 days and challenged i.p. with azoxymethane (10 mg/kg) followed by 2% dextran sodium sulfate (DSS) in the drinking water for 7 days to induce colitis-associated colorectal cancer (CRC). The disease activity index, a composite score reflecting clinical signs of the disease (i.e. perianal soiling, rectal bleeding, diarrhea, and piloerection) was assessed daily for mice undergoing the DSS challenge (A). Mice were euthanized on day 68. Colon and mesenteric lymph nodes (MLN) (B&C) were macroscopically scored for inflammation. Data are represented as mean ± standard error. Points with an asterisk are significantly different when compared to the control group (P<0.05).