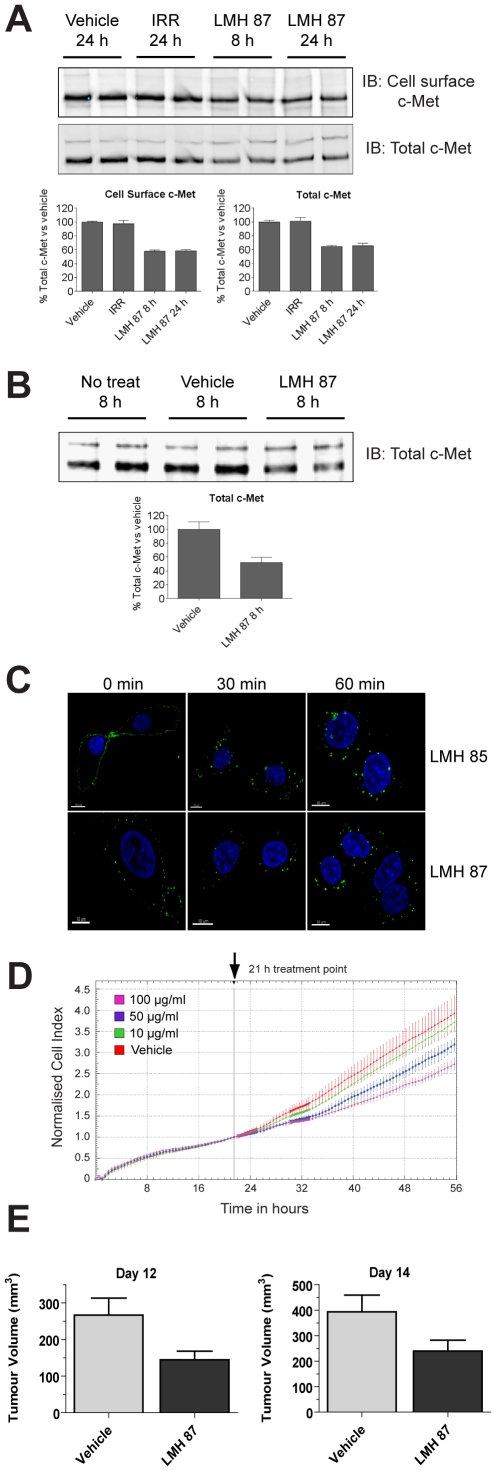
Figure 5. LMH 87 down-regulates surface c-MET and inhibits tumor cell growth.
(A) c-MET was IPed using anti-c-MET antibody coupled to agarose beads from A549 lung cancer cells treated with LMH 87 and then cell surface biotinylated. Cell surface c-MET (upper blot) and total c-MET (lower blot) levels were determined by IB as detailed in the Materials & Methods. Bar graphs show quantification by densitometry ± SEM. IRR = irrelevant antibody. (B) total c-MET remaining in U87MG glioma cells following incubation with LMH 87. Bar graph shows quantification by densitometry ± SEM. Both (A) and (B) are representative blots of repeated experiments. (C) LMH 85 and LMH 87 are internalized following engagement of the c-MET receptor. A549 cells were bound with LMH 85 (top panels) or LMH 87 (bottom panels) followed by AF488- labeled secondary antibody at 4°C. Internalization was induced with addition of media at 37°C. Significant internalization of both antibodies was observed at 30 min and 60 min as indicated by relocation of the fluorescent signal from the membrane to diffuse cytoplasmic and perinuclear locations. Scale bar = 10 µm. (D) xCELLigence analysis of A549 cells treated with LMH 87. A549 cells were treated with vehicle or different concentrations of LMH 87. Data is presented as the cell index normalized to 21 h ± SEM, the time point when antibody was added. Both the 50 and 100 µg/ml treatments caused a significant decrease (p<0.05) in cell index compared to vehicle control. (E) inhibition of U87MG xenograft growth after LMH 87 administration. Mice were implanted with U87MG cells and injected three times (days 7, 10 and 12) with 1 mg of LMH 87 or vehicle. Data is presented as the mean tumor size in mm3 ± SEM. LMH 87 significantly inhibited tumor growth at day 12 (p = 0.014) and day 14 (p = 0.03).