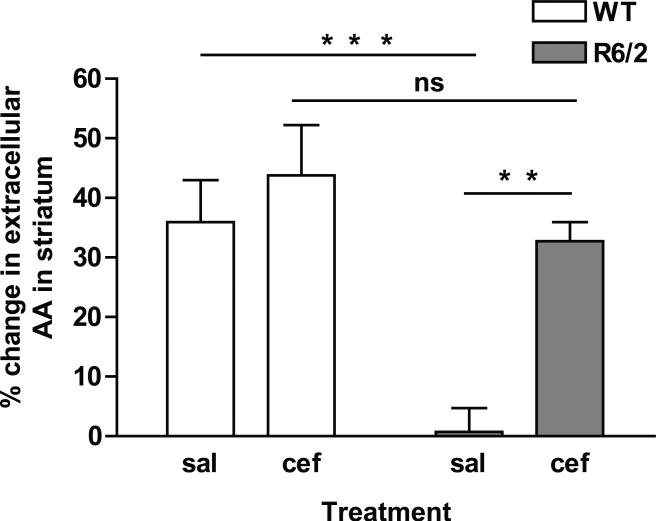
Figure 2.
Ceftriaxone elevates evoked levels of extracellular AA in striatum of R6/2 mice. Data represent the percent change in AA release into striatal extracellular fluid in WT and R6/2 mice treated with either saline (sal) or ceftriaxone (cef). The change in AA was measured by comparing the pre-stimulation voltammetric AA peak height to the post-stimulation peak height. There was a main effect of genotype [F(1,16) = 14.4, p < 0.01] and treatment [F(1,16) = 10.7, p < 0.01]. R6/2sal had little to no increase in extracellular levels of striatal AA following cortical stimulation relative to WT mice. R6/2cef mice, however, had a significantly greater magnitude of striatal AA release than R6/2sal and did not differ from WTcef mice (asterisks represent Tukey test, **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001; ns = not significant; n = 5 for WTsal, n = 5 for WTcef, n = 4 for R6/2sal, n = 6 for R6/2cef).