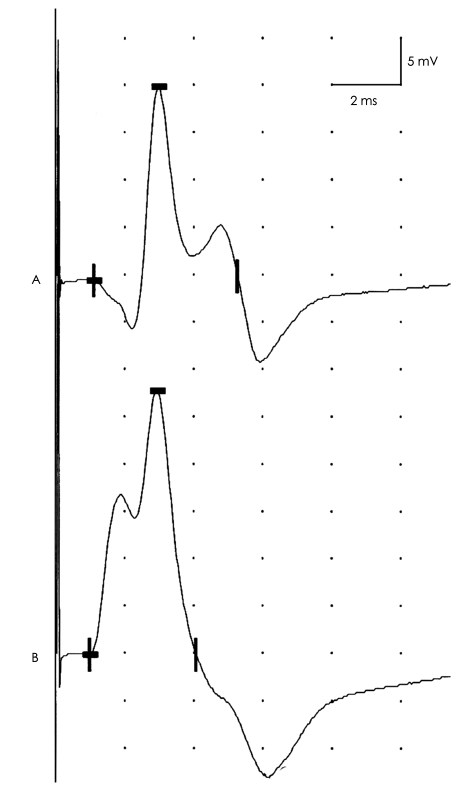
Fig. 9.
Effect of recording electrode position. CMAPs recorded from the adductor digiti minimi in response to ulnar nerve stimulation at the wrist. Attachment of the active electrode slightly away from the muscle's motor point results in an initial positive deflection and reduced CMAP amplitude (A). By relocating the active electrode to directly above the muscle's motor point, an initially negative biphasic CMAP is observed with increased amplitude (B). When a CMAP has an initial positive deflection, the active electrode should be relocated to the assumed motor point. CMAP: compound muscle action potential.