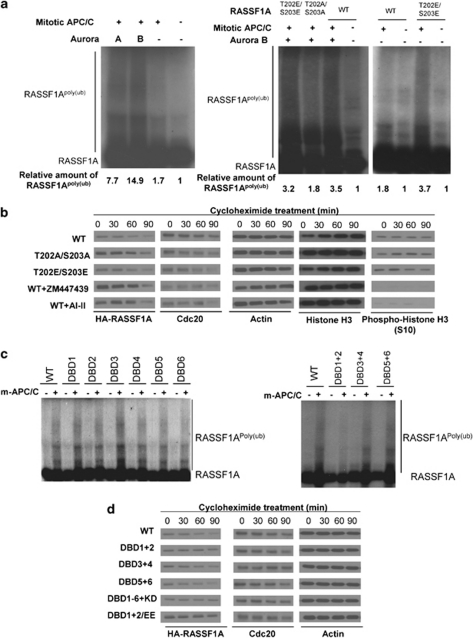
Figure 5.
Aurora kinases facilitated the ubiquitination and degradation of RASSF1A. (a) Aurora kinases facilitated the ubiquitination of RASSF1A by purified mitotic APC/C in vitro. The in vitro ubiquitination reaction was set up using APC/C purified from mitotic HeLa cells. (Left panel) 35S-labeled RASSF1A was used as substrate. (Right panel) 35S-labeled wild-type or phospho-mutants of RASSF1A were used as substrate. Where indicated, Aurora A or Aurora B was added. (b) Phosphorylation of RASSF1A by Aurora kinases is essential for Cdc20-dependent degradation. HeLa cells were transfected with different mutants of HA-RASSF1A. After 24 h, cells were arrested to mitosis by nocodazole. Where indicated, cells were treated with 2 μ ZM447439 or 2 μ AI-II for 2 h. The cells were then treated with 50 μg/ml cycloheximide (CHX) and collected at indicated time points for immunoblotting. (c) APC/CCdc20 ubiquitinates RASSF1A at DB1 and DB2 in vitro. Wild-type or mutated 35S-labeled RASSF1A was subjected to in vitro ubiquitination assay using mitotic HeLa APC/C and purified Aurora B. RASSF1A was resistant to APC/C ubiquitination when both DB1 and DB2 were deleted. (d) DB1 and DB2 of RASSF1A are essential for Cdc20-dependent degradation in vivo. HeLa cells were transfected with different HA-RASSF1A mutants and treated as in (b). Consistent with in vitro ubiquitination assay, RASSF1ADBD1+2 mutant was resistant to Cdc20-dependent degradation.