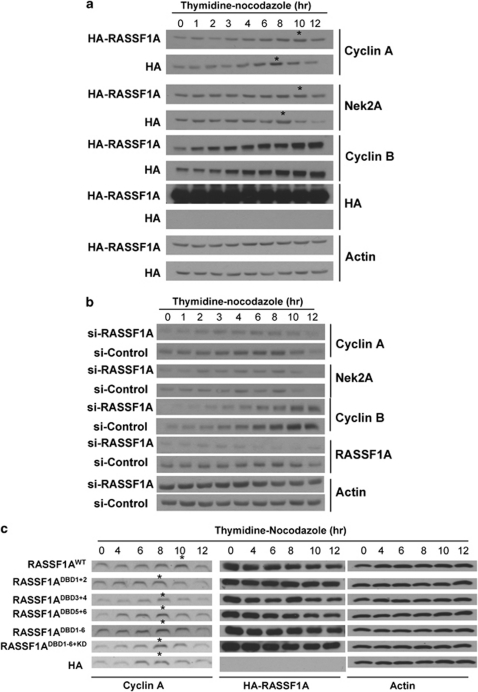
Figure 6.
(a) RASSF1A delays Cyclin A degradation during mitosis. HeLa cells transfected with HA-RASSF1A were synchronized by thymidine block and released into nocodazole. Cells were collected at indicated time points for immunoblotting (left panel). Cyclin A and Nek2A were not degraded until 10 h post-thymidine block in cells transfected with HA-RASSF1A, whereas it was degraded at 8 h in control cells. (b) RASSF1A promotes accumulation of Cyclin A. HeLa cells transfected with siRNA targeting RASSF1A were synchronized and analyzed as in Figure 2b. The level of Cyclin A was consistently lower in cells transfected with RASSF1A siRNA than those transfected with control siRNA throughout the assay. (c) D-box-deleted RASSF1A mutants fail to delay the degradation of Cyclin A during mitosis. HeLa cells transfected with D-box-deleted mutants of RASSF1A were synchronized and analyzed as in (b). The immunoblotting was performed (upper panel). Although RASSF1AWT delayed the degradation of Cyclin A after the thymidine block, none of the RASSF1ADBD mutants delayed the degradation of Cyclin A. *Time point when Cyclin A degradation started.