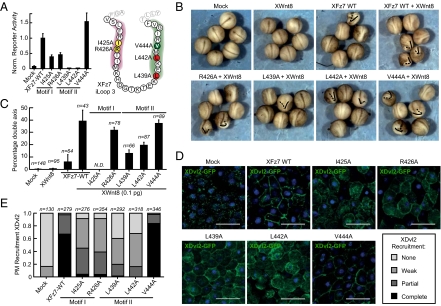
Fig. 3.
XFz7 motifs I and II are essential for Wnt-mediated signaling and XDvl2 recruitment in Xenopus embryos. (A) XFz7 iLoop3 motif I and II mutants display decreased Wnt3a-induced signaling. Indicated motif I and II XFz7 mutants were tested in the TOPFlash luciferase reporter assay as in Fig. 2A. (Left) Shown are the average normalized values of three individual experiments; error bars indicate SDs. Mock, empty vector. (Right) Color-coded activity map of tested XFz7 iLoop3 residues (as in Fig. 2C). (B) XFz7 motif II mutants are defective in secondary axis formation in Xenopus embryos. Ventral injections of combined mRNAs encoding for XFz7 variants and XWnt8 were used to compare β-catenin–mediated secondary axis formation. The primary axis is indicated by straight lines, and (partial) secondary axes are indicated by dotted lines. (C) Quantification of the results presented in B. XFz7 I425A caused severe embryonic lethality and was not quantified. Shown are the average percentages of axis duplication of three independent experiments; error bars depict SEs. The number of counted embryos per condition is indicated. (D) Colocalization of XFz7 motif I and II mutants and XDvl2-GFP in Xenopus animal cap explants is impaired. (Scale bars: 100 μm.) (E) Quantification of the results in D (as in Fig. 2 D and E). The number of counted cells is indicated.