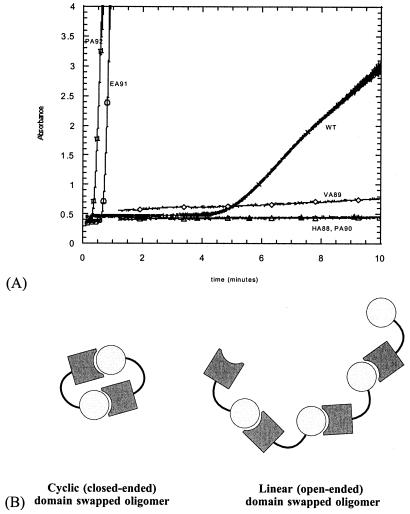
Figure 3.
Relationship between domain swapping and aggregation in suc1. (A) Kinetics of aggregation of wild-type suc1 (crosses) and hinge mutants HA88 (closed triangles), VA89 (diamonds), PA90 (open triangles), EA91 (circles), and PA92 (squares). Mutation to alanine of the residues in the first half of the hinge (H88, V89, P90) slows down aggregation of suc1, whereas it is accelerated by mutation of the residues in the second half of the hinge (E91, P92). (B) Schematic showing how strand exchange can occur between two monomers to form a “closed-ended” dimer pair or between adjacent monomers in an “open-ended” high-order oligomer.